The mammalian calcium-binding protein, nucleobindin (CALNUC), is a Golgi resident protein
- PMID: 9647645
- PMCID: PMC2132997
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.7.1515
The mammalian calcium-binding protein, nucleobindin (CALNUC), is a Golgi resident protein
Abstract
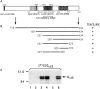
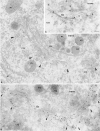
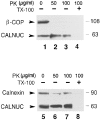
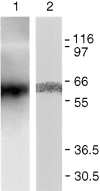
We have identified CALNUC, an EF-hand, Ca2+-binding protein, as a Golgi resident protein. CALNUC corresponds to a previously identified EF-hand/calcium-binding protein known as nucleobindin. CALNUC interacts with Galphai3 subunits in the yeast two-hybrid system and in GST-CALNUC pull-down assays. Analysis of deletion mutants demonstrated that the EF-hand and intervening acidic regions are the site of CALNUC's interaction with Galphai3. CALNUC is found in both cytosolic and membrane fractions. The membrane pool is tightly associated with the luminal surface of Golgi membranes. CALNUC is widely expressed, as it is detected by immunofluorescence in the Golgi region of all tissues and cell lines examined. By immunoelectron microscopy, CALNUC is localized to cis-Golgi cisternae and the cis-Golgi network (CGN). CALNUC is the major Ca2+-binding protein detected by 45Ca2+-binding assay on Golgi fractions. The properties of CALNUC and its high homology to calreticulin suggest that it may play a key role in calcium homeostasis in the CGN and cis-Golgi cisternae.
Figures




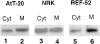




References
-
- Baksh, S., and M. Michalak. 1996. Basic characteristics and ion binding to calreticulin. In Calreticulin. M. Michalak, editor. R.G. Landes Company, Georgetown. 11–26.
-
- Booth C, Koch GLE. Perturbation of cellular calcium induces secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1989;59:729–737. - PubMed
-
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1991;256:1604–1607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

