Microbial Community Composition of Wadden Sea Sediments as Revealed by Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
- PMID: 9647850
- PMCID: PMC106446
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.7.2691-2696.1998
Microbial Community Composition of Wadden Sea Sediments as Revealed by Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
Abstract
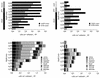
The microbial community composition of Wadden Sea sediments of the German North Sea coast was investigated by in situ hybridization with group-specific fluorescently labeled, rRNA-targeted oligonucleotides. A large fraction (up to 73%) of the DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole)-stained cells hybridized with the bacterial probes. Nearly 45% of the total cells could be further identified as belonging to known phyla. Members of the Cytophaga-Flavobacterium cluster were most abundant in all layers, followed by the sulfate-reducing bacteria.
Figures

References
-
- Cammen L M. Annual bacterial production in relation to benthic microalgal production and sediment oxygen uptake in an intertidal sandflat and an intertidal mudflat. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 1991;71:13–25.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

