Design and Application of Two Rapid Screening Techniques for Isolation of Mn(IV) Reduction-Deficient Mutants of Shewanella putrefaciens
- PMID: 9647855
- PMCID: PMC106451
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.7.2716-2720.1998
Design and Application of Two Rapid Screening Techniques for Isolation of Mn(IV) Reduction-Deficient Mutants of Shewanella putrefaciens
Abstract
Chemical mutagenesis procedures and two newly developed rapid plate assays were used to identify two Mn(IV) reduction-deficient (Mnr) mutants of Shewanella putrefaciens. All eleven members of a set of previously isolated Fe(III) reduction-deficient (Fer) mutants displayed Mnr-positive phenotypes on the plate assays and were also capable of anaerobic growth on Mn(IV) as the sole terminal electron acceptor.
Figures

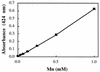

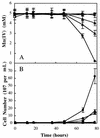
 ), Mn(IV) (□), or cells
(⧫) were omitted. The initial cell density was (1 ± 0.2) ×
107 cells per ml for each culture. Mn(IV) was determined
colorimetrically, and acridine orange-stained cells were counted
directly. Values are means of three parallel but independent anaerobic
incubations; error bars represent standard deviations. Some of the
error bars cannot be seen due to the small standard deviations.
), Mn(IV) (□), or cells
(⧫) were omitted. The initial cell density was (1 ± 0.2) ×
107 cells per ml for each culture. Mn(IV) was determined
colorimetrically, and acridine orange-stained cells were counted
directly. Values are means of three parallel but independent anaerobic
incubations; error bars represent standard deviations. Some of the
error bars cannot be seen due to the small standard deviations.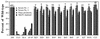
References
-
- Balistrieri L S, Murray J W, Paul B. The cycling of iron and manganese in the water column of Lake Sammamish, Washington. Limnol Oceanogr. 1992;37:510–528.
-
- Burns R G, Burns V M. Manganese oxides. In: Burns R G, editor. Marine minerals. Washington, D.C: Mineralogical Society of America; 1979. pp. 1–40.
-
- Canfield D E. Sulfate reduction and oxic respiration in marine sediments: implications for organic carbon preservation in euxinic environments. Deep-Sea Res. 1989;36:121–138. - PubMed
-
- Christensen J P, Murray J W, Devol A H, Codispoti L A. Denitrification in coastal shelf sediments has major impact on the oceanic nitrogen budget. Global Biogeochem Cycles. 1987;1:97–116.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

