Identification of Xenopus SMC protein complexes required for sister chromatid cohesion
- PMID: 9649503
- PMCID: PMC316973
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.13.1986
Identification of Xenopus SMC protein complexes required for sister chromatid cohesion
Abstract
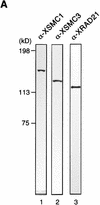
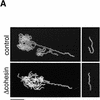
The structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) family is a growing family of chromosomal ATPases. The founding class of SMC protein complexes, condensins, plays a central role in mitotic chromosome condensation. We report here a new class of SMC protein complexes containing XSMC1 and XSMC3, Xenopus homologs of yeast Smc1p and Smc3p, respectively. The protein complexes (termed cohesins) exist as two major forms with sedimentation coefficients of 9S and 14S. 9S cohesin is a heterodimer of XSMC1 and XSMC3, whereas 14S cohesin contains three additional subunits. One of them has been identified as a Xenopus homolog of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rad21p implicated in DNA repair and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Scc1p/Mcd1p implicated in sister chromatid cohesion. 14S cohesin binds to interphase chromatin independently of DNA replication and dissociates from it at the onset of mitosis. Immunodepletion of cohesins during interphase causes defects in sister chromatid cohesion in subsequent mitosis, whereas condensation is unaffected. These results suggest that proper assembly of mitotic chromosomes is regulated by two distinct classes of SMC protein complexes, cohesins and condensins.
Figures
















References
-
- Benavente R, Krohne G, Franke WW. Cell type-specific expression of nuclear lamina proteins during development of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1985;41:177–790. - PubMed
-
- Blow JJ, Laskey RA. Initiation of DNA replication in nuclei and purified DNA by a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1986;47:577–587. - PubMed
-
- Castaño IB, Brzoska PM, Sadoff BU, Chen H, Christman MF. Mitotic chromosome condensation in the rDNA requires TRF4 and DNA topoisomerase I in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes & Dev. 1996;10:2564–2576. - PubMed
-
- Coleman TR, Carpenter PB, Dunphy WG. The Xenopus cdc6 protein is essential for the initiation of a single round of DNA replication in cell-free extracts. Cell. 1996;87:53–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
