Activation of the A2A adenosine receptor inhibits nitric oxide production in glial cells
- PMID: 9650577
- PMCID: PMC5454773
- DOI: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)00556-0
Activation of the A2A adenosine receptor inhibits nitric oxide production in glial cells
Abstract
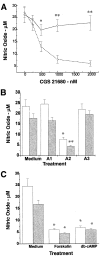
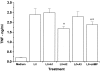
Selective adenosine receptor agonists and antagonists have marked effects on the outcome of cerebral ischemia, and adenosine receptors are expressed on astrocytes. In this study we examined the effects of various adenosine receptor agonists on the production of nitric oxide and the induction of iNOS in astrocytes activated by LPS/IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha/IL-1beta and on the production of TNF-alpha. Treatment of the cells with the A2A receptor agonist CGS 21680 inhibited both NO production and iNOS expression induced by stimulation with either LPS/IFN-gamma or TNF-alpha/IL-1beta, whereas the A1 and A3 receptor agonists, CPA and Cl-IB-MECA, respectively, did not have significant inhibitory effects. The inhibitory effect of the A2A receptor agonist was antagonized by the specific A2A receptor antagonist CSC. The A2A agonist also exerted a small inhibitory effect on the production of TNF-alpha. Similar inhibitory effects on the production of NO were obtained by cyclic AMP-elevating reagents, such as forskolin and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Our findings suggest that activation of the A2A receptor inhibits NO production and iNOS expression likely via increased cAMP.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

