Diagnosis of Q fever
- PMID: 9650920
- PMCID: PMC104936
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.7.1823-1834.1998
Diagnosis of Q fever
Figures

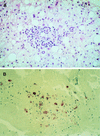
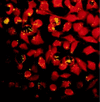
References
-
- Aitken I D, Bogel K, Cracea E, Edlinger E, Houwers D, Krauss H, Rady M, Rehacek J, Schiefer H G, Schmeer N, et al. Q fever in Europe: current aspects of aetiology, epidemiology, human infection, diagnosis and therapy. Infection. 1987;15:323–327. - PubMed
-
- Babudieri B. Q fever: a zoonosis. Adv Vet Sci. 1959;5:81–182.
-
- Bachaud M, Massip P, Boneu B, Armengaud M. Inhibiteur acquis du facteur anti-hémophilique B (facteur IX) au cours d’une fièvre Q. Rev Med Toulouse. 1983;1:229–231.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

