Detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of pigs by PCR
- PMID: 9650949
- PMCID: PMC104965
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.7.1984-1988.1998
Detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of pigs by PCR
Abstract
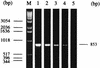
In the present investigation we developed a method for the detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of pigs by PCR with a primer pair flanking a DNA fragment of 853 bp specific for M. hyopneumoniae. Several methods were tested to eliminate the amplification inhibitors present in BALFs. The best results were obtained by the extraction of the DNA from the BALFs. By the PCR performed with the extracted DNA, 10(2) CFU of M. hyopneumoniae could be detected in 1 ml of BALF from specific-pathogen-free swine experimentally inoculated with M. hyopneumoniae. DNA from 11 other mycoplasma species and 17 cell-walled bacterial species colonizing the respiratory tracts of pigs was not amplified. In a field study BALFs from 40 pigs from farms with a history of chronic pneumonia were tested for M. hyopneumoniae by cultivation and by PCR (i) with BALFs incubated in Friis medium and (ii) with DNA extracted from the BALFs. In addition, PCR was performed with postmortem lung washings from 19 of the 40 pigs, and immunofluorescence tests were carried out with sections of lungs from 18 of the 40 pigs. M. hyopneumoniae could not be detected in 18 of the 40 pigs by any of the five methods tested. The remaining 22 pigs showed a positive reaction by the PCR with DNA extracted from the BALFs and variable positive reactions by the other tests. A complete correspondence could be observed between the immunofluorescence test result and the result of PCR with DNA. The investigation shows that the PCR with DNA extracted from BALFs is a suitable technique for the sensitive and specific in vivo detection of M. hyopneumoniae.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polymerase chain reaction for Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae detection in tracheobronchiolar washings from pigs.Mol Cell Probes. 1996 Feb;10(1):15-22. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.1996.0003. Mol Cell Probes. 1996. PMID: 8684372
-
Use of an internal control in a nested-PCR assay for Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae detection and quantification in tracheobronchiolar washings from pigs.Mol Cell Probes. 2000 Dec;14(6):365-72. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.2000.0326. Mol Cell Probes. 2000. PMID: 11090266
-
Diagnosis and differentiation of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Mycoplasma hyorhinis infections in pigs by PCR amplification of the p36 and p46 genes.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Apr;38(4):1390-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.4.1390-1396.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10747113 Free PMC article.
-
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae: interaction with other agents in pigs, and evaluation of immunogens.Arch Med Res. 1994 Summer;25(2):235-9. Arch Med Res. 1994. PMID: 7919820 Review.
-
Swine mycoplasmoses.Rev Sci Tech. 1996 Dec;15(4):1569-605. doi: 10.20506/rst.15.4.983. Rev Sci Tech. 1996. PMID: 9190026 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective medium for culture of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.Vet Microbiol. 2016 Nov 15;195:158-164. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.09.022. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Vet Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27771062 Free PMC article.
-
The occurrence of mycoplasmas in the lungs of swine in Gran Canaria (Spain).Vet Res Commun. 2005 Aug;29(6):453-62. doi: 10.1007/s11259-005-1866-3. Vet Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 16215836
-
Clinical use of capillary PCR to diagnose Mycoplasma pneumonia.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Apr;38(4):1382-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.4.1382-1384.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10747111 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae by polymerase chain reaction in swine presenting respiratory problems.Braz J Microbiol. 2008 Jul;39(3):471-6. doi: 10.1590/S1517-838220080003000011. Epub 2008 Sep 1. Braz J Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 24031248 Free PMC article.
-
A Unique Capsule Locus in the Newly Designated Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae Serovar 16 and Development of a Diagnostic PCR Assay.J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Mar;55(3):902-907. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02166-16. Epub 2017 Jan 4. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28053219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abiven P, Pommier P. Technique de lavage tracheobronchique par la voie transnasal pour la détection de Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae chez le porc vivant non anesthésie. Vet Res. 1993;24:515–522. - PubMed
-
- Artiushin S, Stipkovits L, Minion F C. Development of polymerase chain reaction primers to detect Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Mol Cell Probes. 1993;7:381–385. - PubMed
-
- Bej A K, Mahbubani M H, Atlas R M. Amplification of nucleic acids by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and other methods and their applications. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26:301–334. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

