Survey of incidence of Clostridium difficile infection in Canadian hospitals and diagnostic approaches
- PMID: 9650966
- PMCID: PMC104982
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.7.2076-2080.1998
Survey of incidence of Clostridium difficile infection in Canadian hospitals and diagnostic approaches
Abstract
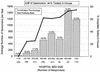
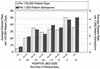
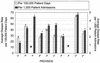
A questionnaire relating to Clostridium difficile disease incidence and diagnostic practices was sent to 380 Canadian hospitals (all with > 50 beds). The national questionnaire response rate was 63%. In-house testing was performed in 17.6, 61.5, and 74.2% of the hospitals with < 300, 300 to 500, and > 500 beds, respectively. The average test positivity rates were 17.2, 15.3, and 13.2% for hospitals with < 300, 300 to 500, and > 500 beds, respectively. The average disease incidences were 23.5, 30.8, and 40.3 cases per 100,000 patient days in the hospitals with < 300, 300 to 500, and > 500 beds, respectively. In the 81 hospitals where in-house testing was performed, cytotoxin testing utilizing tissue culture was most common (44.4%), followed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (38.3%), culture for toxigenic C. difficile (32.1%), and latex agglutination (13.6%). The clinical criteria for C. difficile testing were variable, with 85% of hospitals indicating that a test was done automatically if ordered by a doctor. Our results show that C. difficile-associated diarrhea is a major problem in hospitals with > or = 200 beds. Despite a lower disease incidence in smaller hospitals, there was a higher diagnostic test positivity rate. This may reflect the preference of smaller hospitals for culture and latex agglutination tests.
Figures

References
-
- Aronsson B, Mollby R, Nord C E. Antimicrobial agents and Clostridium difficile in acute enteric disease: epidemiological data from Sweden, 1980–1982. J Infect Dis. 1985;151:476–481. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett J. Clostridium difficile: clinical considerations. Rev Infect Dis. 1990;12:S243–S251. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett J G. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;15:573–581. - PubMed
-
- Bender B S, Bennett R, Laughon B E, Greenough W B, Gaydos C, Sears S D, Forman M S, Bartlett J G. Is Clostridium difficile endemic in chronic-care facilities? Lancet. 1986;ii:11–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

