The sodium channel Scn8a is the major contributor to the postnatal developmental increase of sodium current density in spinal motoneurons
- PMID: 9651206
- PMCID: PMC6793491
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-14-05234.1998
The sodium channel Scn8a is the major contributor to the postnatal developmental increase of sodium current density in spinal motoneurons
Abstract
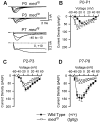
Sodium currents were recorded from motoneurons that were isolated from mice at postnatal days 0-8 (P0-P8) and maintained in culture for 12-24 hr. Motoneurons from normal mice exhibited a more than threefold increase in peak sodium current density from P0 to P8. For mice lacking a functional Scn8a sodium channel gene, motoneuronal sodium current density was comparable at P0 to that of normal mice but failed to increase from P0 to P8. The absence of Scn8a sodium channels is associated with the phenotype "motor end plate disease," which is characterized by a progressive neuromuscular failure and is fatal by 3-4 postnatal weeks. Thus, it appears that the development and function of mature motoneurons depends on the postnatal induction of Scn8a expression.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The absence of resurgent sodium current in mouse spinal neurons.Brain Res. 1999 Dec 4;849(1-2):162-8. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)02060-0. Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10592298
-
The neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel, Scn8a, is essential for postnatal maturation of spinal, but not oculomotor, motor units.Exp Neurol. 1996 Jun;139(2):328-34. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1996.0107. Exp Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8654536
-
Postnatal changes in the inactivation properties of voltage-gated sodium channels contribute to the mature firing pattern of spinal motoneurons.J Neurophysiol. 2008 Jun;99(6):2864-76. doi: 10.1152/jn.00059.2008. Epub 2008 Apr 9. J Neurophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18400961
-
Allelic mutations of the sodium channel SCN8A reveal multiple cellular and physiological functions.Genetica. 2004 Sep;122(1):37-45. doi: 10.1007/s10709-004-1441-9. Genetica. 2004. PMID: 15619959 Review.
-
Voltage-sensitive ion channels in rhythmic motor systems.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002 Dec;12(6):646-51. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(02)00377-x. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 12490254 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional analysis of the mouse Scn8a sodium channel.J Neurosci. 1998 Aug 15;18(16):6093-102. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-16-06093.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9698304 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of emerging excitability in rat embryonic motoneurons.J Physiol. 2002 May 15;541(Pt 1):25-39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013371. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12015418 Free PMC article.
-
Current injection and receptor-mediated excitation produce similar maximal firing rates in hypoglossal motoneurons.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Mar;115(3):1307-13. doi: 10.1152/jn.00848.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 26745245 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive Properties and Powerful Neuromodulation of Nav1.6 Sodium Channels Regulates Neuronal Excitability.Cells. 2021 Jun 25;10(7):1595. doi: 10.3390/cells10071595. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34202119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-dependent reduction in voltage-gated inward sodium current and Scn8a gene expression in murine stellate ganglia.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2025 Mar;1545(1):91-104. doi: 10.1111/nyas.15298. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2025. PMID: 39998310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyd IA, Davey MR. Composition of peripheral nerves. Livingstone; Edinburgh: 1968.
-
- Burgess DL, Kohrman DC, Galt J, Plummer NW, Jones JM, Spear B, Meisler MH. Mutation of a new sodium channel gene, Scn8a, in the mouse mutant “motor endplate disease.”. Nat Genet. 1995;10:461–465. - PubMed
-
- Dick DJ, Boakes RJ, Candy JM, Harris JB, Cullen MJ. Cerebellar structure and function in the murine mutant “jolting.”. J Neurol Sci. 1986;76:255–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
