G-Protein-dependent facilitation of neuronal alpha1A, alpha1B, and alpha1E Ca channels
- PMID: 9651207
- PMCID: PMC6793477
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-14-05240.1998
G-Protein-dependent facilitation of neuronal alpha1A, alpha1B, and alpha1E Ca channels
Abstract
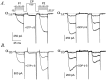
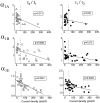
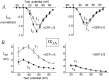
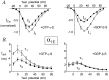
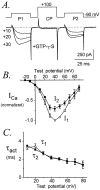
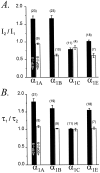
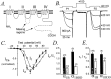
Modulation of neuronal voltage-gated Ca channels has important implications for synaptic function. To investigate the mechanisms of Ca channel modulation, we compared the G-protein-dependent facilitation of three neuronal Ca channels. alpha1A, alpha1B, or alpha1E subunits were transiently coexpressed with alpha2-deltab and beta3 subunits in HEK293 cells, and whole-cell currents were recorded. After intracellular dialysis with GTPgammaS, strongly depolarized conditioning pulses facilitated currents mediated by each Ca channel type. The magnitude of facilitation depended on current density, with low-density currents being most strongly facilitated and high-density currents often lacking facilitation. Facilitating depolarizations speeded channel activation approximately 1.7-fold for alpha1A and alpha1B and increased current amplitudes by the same proportion, demonstrating equivalent facilitation of G-protein-inhibited alpha1A and alpha1B channels. Inactivation typically obscured facilitation of alpha1E current amplitudes, but the activation kinetics of alpha1E currents showed consistent and pronounced G-protein-dependent facilitation. The onset and decay of facilitation had the same kinetics for alpha1A, alpha1B, and alpha1E, suggesting that Gbeta gamma dimers dissociate from and reassociate with these Ca channels at very similar rates. To investigate the structural basis for N-type Ca channel modulation, we expressed a mutant of alpha1B missing large segments of the II-III loop and C terminus. This deletion mutant exhibited undiminished G-protein-dependent facilitation, demonstrating that a Gbeta gamma interaction site recently identified within the C terminus of alpha1E is not required for modulation of alpha1B.
Figures




References
-
- Bean BP. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989;340:153–156. - PubMed
-
- Bernheim L, Beech DJ, Hille B. A diffusible second messenger mediates one of the pathways coupling receptors to calcium channels in rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1991;6:859–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
