Role of the nucleus raphe magnus in antinociception produced by ABT-594: immediate early gene responses possibly linked to neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on serotonergic neurons
- PMID: 9651224
- PMCID: PMC6793487
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-14-05426.1998
Role of the nucleus raphe magnus in antinociception produced by ABT-594: immediate early gene responses possibly linked to neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on serotonergic neurons
Abstract
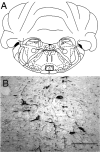
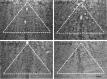
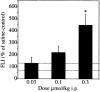
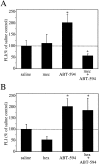
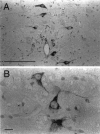
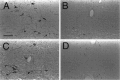
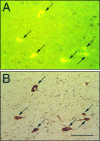
Recently, a novel cholinergic channel modulator, (R)-5-(2-azetidinylmethoxy)-2-chloropyridine (ABT-594), was shown to produce potent analgesia in a variety of rodent pain models when administered either systemically or centrally into the nucleus raphe magnus (NRM). The purpose of the present study was to investigate the possible supraspinal contribution of ABT-594 by assessing its ability to induce expression of the immediate early gene c-fos, a biochemical marker of neuronal activation, in the NRM of rats. Putative serotonergic neurons in the NRM, a medullary nucleus proposed to be involved in descending antinociceptive pathways, were identified immunohistochemically using a monoclonal antibody (mAb) against tryptophan hydroxylase. ABT-594 (0.03-0.3 micromol/kg, i.p.) produced a dose-dependent induction of Fos protein that was blocked by the central nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) antagonist mecamylamine (5 micromol/kg, i.p.) but not by the peripheral nAChR antagonist hexamethonium (15 micromol/kg, i.p.). Immunohistological studies using mAb 299 revealed the expression of alpha4-containing nAChRs in the NRM. The alpha4 immunostaining was dramatically reduced by pretreating (30 d) animals with the serotonin neurotoxin 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine (5,7-DHT), which was previously shown to substantially attenuate the antinociceptive actions of ABT-594. In a double immunohistochemical labeling experiment, coexpression of the serotonin marker tryptophan hxdroxylase and the alpha4 nAChR subunit in NRM neurons was observed. These results suggest that the analgesic mechanism of ABT-594 may in part involve the activation of the NRM, a site where alpha4-containing nAChRs are expressed by serotonergic neurons.
Figures
References
-
- Bannon AW, Decker MW, Holladay MW, Curzon P, Donnelly-Roberts D, Puttfarcken PS, Bitner RS, Diaz A, Dickenson AH, Williams M, Arneric SP. Broad spectrum, non-opioid analgesic activity by selective modulation of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Science. 1998;279:77–81. - PubMed
-
- Basbaum AI, Fields HL. The origin of descending pathways in the dorsolateral funiculus of the spinal cord of the cat and rat: further studies on the anatomy of pain modulation. J Comp Neurol. 1979;187:513–532. - PubMed
-
- Bitner RS, Nikkel AL, Bannon AW, Arneric SP, Decker MW. Supraspinal C-fos induction produced by a novel cholinergic channel modulator analgesic, ABT-594. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1997;23:1200.
-
- Bowker RM, Westlund KN, Sullivan MC, Coulter JD. Organization of descending serotonergic projections to the spinal cord. Prog Brain Res. 1982;57:239–265. - PubMed
-
- Brodie MS, Proudfit HK. Antinociception induced by local injections of carbachol into the nucleus raphe magnus in rats: alteration by intrathecal injection of monoaminergic antagonists. Brain Res. 1986;371:70–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
