Efficient adenoviral infection with IkappaB alpha reveals that macrophage tumor necrosis factor alpha production in rheumatoid arthritis is NF-kappaB dependent
- PMID: 9653166
- PMCID: PMC20955
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.8211
Efficient adenoviral infection with IkappaB alpha reveals that macrophage tumor necrosis factor alpha production in rheumatoid arthritis is NF-kappaB dependent
Abstract
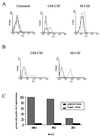
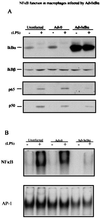
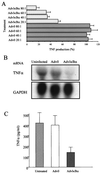
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha has been shown to be a major therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis with the success of anti-TNFalpha antibody clinical trials. Although signaling pathways leading to TNFalpha expression have been studied in some detail, there is evidence for considerable differences between individual cell types. This prompted us to investigate the intracellular signaling pathways that result in increased TNFalpha synthesis from macrophages in the diseased synovial joint tissue. Using an adenoviral system in vitro we report the successful delivery of genes to more than 95% of normal human macrophages. This permitted us to show, by using adenoviral transfer of IkappaB alpha, the natural inhibitor of NF-kappaB, that induction of TNFalpha in normal human macrophages by lipopolysaccharide, but not by some other stimuli, was inhibited by 80%. Furthermore the spontaneous production of TNFalpha from human rheumatoid joint cell cultures was inhibited by 75%, indicating that the NF-kappaB pathway is an essential step for TNFalpha synthesis in synovial macrophages and demonstrating that NF-kappaB should be an effective therapeutic target in this disease.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

