Targeted disruption of the interferon-gamma receptor 2 gene results in severe immune defects in mice
- PMID: 9653170
- PMCID: PMC20959
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.8233
Targeted disruption of the interferon-gamma receptor 2 gene results in severe immune defects in mice
Abstract
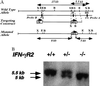
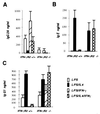
To study the role of the interferon- (IFN) gammaR2 chain in IFN-gamma signaling and immune function, IFN-gammaR2-deficient mice have been generated and characterized. Cells derived from IFN-gammaR2 -/- mice are unable to activate either JAK/STAT signaling proteins or gene transcription in response to IFN-gamma. The lack of IFN-gamma responsiveness alters IFN-gamma-induced Ig class switching by B cells from these mice. In vitro cultures of T cells demonstrate that the T cells from the IFN-gammaR2 -/- mice have a defect in Th1 cell differentiation. The IFN-gammaR2 (-/-) mice also produce lower amounts of IFN-gamma in response to antigenic challenge. In addition, IFN-gammaR2 -/- mice are defective in contact hypersensitivity and are highly susceptible to infection by Listeria monocytogenes. These results demonstrate that the IFN-gammaR2 is essential for IFN-gamma-mediated immune responses in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- Farrar M A, Schreiber R D. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:571–611. - PubMed
-
- Pestka S, Langer J A, Zoon K C, Samuel C E. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. - PubMed
-
- Pestka S, Kotenko S V, Muthukumaran G, Izotova L S, Cook J R, Garotta G. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997;8:189–206. - PubMed
-
- Bach E A, Aguet M, Schreier R D. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:563–591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

