Involvement of human CRM1 (exportin 1) in the export and multimerization of the Rex protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1
- PMID: 9658105
- PMCID: PMC109841
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.8.6602-6607.1998
Involvement of human CRM1 (exportin 1) in the export and multimerization of the Rex protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1
Abstract
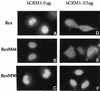
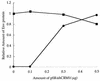
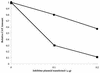
We investigated the role of human CRM1 (hCRM1) (exportin 1) in the function of Rex protein encoded by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. hCRM1 promoted the export of Rex protein from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. A Rex protein with a mutation in the activation domain, RexM90, lost both the ability to bind to hCRM1 and the ability to multimerize. The overexpression of hCRM1 complemented the functional defects of RexM64, which contains a mutation in the multimerization domain of Rex. A dominant-negative mutant of Rex which sequesters cofactors of Rex abrogated multimerization as well as the activity of the wild-type Rex protein. These two functions were simultaneously restored by the overexpression of hCRM1. Taken together, these results suggest that hCRM1 plays important roles in the multimerization and export of Rex protein.
Figures
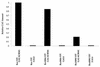



Similar articles
-
A multifunctional domain in human CRM1 (exportin 1) mediates RanBP3 binding and multimerization of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Rex protein.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Dec;23(23):8751-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.23.8751-8761.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14612415 Free PMC article.
-
Rat CRM1 is responsible for the poor activity of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Rex protein in rat cells.J Virol. 2001 Dec;75(23):11515-25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.23.11515-11525.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11689633 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus Rev and human T-cell leukemia virus Rex function, but not Mason-Pfizer monkey virus constitutive transport element activity, by a mutant human nucleoporin targeted to Crm1.J Virol. 1998 Nov;72(11):8627-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.8627-8635.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9765402 Free PMC article.
-
Using retroviruses to study the nuclear export of mRNA.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002;35:151-68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-44603-3_8. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002. PMID: 11791405 Review. No abstract available.
-
The human T-cell leukemia virus Rex protein.Front Biosci. 2005 Jan 1;10:431-45. doi: 10.2741/1539. Print 2005 Jan 1. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15574380 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered expression of tyrosine kinases of the Src and Syk families in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected T-cell lines.J Virol. 1999 May;73(5):3709-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.5.3709-3717.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10196263 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of the Mechanism of Host NMD Suppression by HTLV-1 Rex: Dissection of Rex to Identify the NMD Inhibitory Domain.Viruses. 2022 Feb 9;14(2):344. doi: 10.3390/v14020344. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215946 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning Rex rules HTLV-1 pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 16;13:959962. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.959962. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36189216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral regulation of mRNA export.J Virol. 2004 May;78(9):4389-96. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.9.4389-4396.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15078920 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mutational analysis of bovine leukemia virus Rex: identification of a dominant-negative inhibitor.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(11):7172-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.11.7172-7181.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15890956 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

