Infectious laryngotracheitis herpesvirus expresses a related pair of unique nuclear proteins which are encoded by split genes located at the right end of the UL genome region
- PMID: 9658136
- PMCID: PMC109896
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.8.6867-6874.1998
Infectious laryngotracheitis herpesvirus expresses a related pair of unique nuclear proteins which are encoded by split genes located at the right end of the UL genome region
Abstract
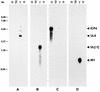
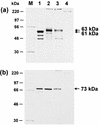
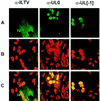
Avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) possesses an alphaherpesvirus type D DNA genome of ca. 155 kbp. Completion of our previous sequence analyses (W. Fuchs and T. C. Mettenleiter, J. Gen. Virol. 77:2221-2229, 1996) of the right end of the unique long (UL) genome region revealed the presence of two adjacent, presumably ILTV-specific genes, which were named UL0 and UL[-1] because of their location upstream of the conserved UL1 (glycoprotein L) gene. Transcriptional analyses showed that both genes are abundantly expressed during the late phase of the viral replication cycle and that both mRNAs are spliced by the removal of short introns close to their 5' ends. Furthermore, the deduced gene products exhibit a moderate but significant homology of 28% to each other. The newly identified ILTV genes encode proteins of 63 kDa (UL0) and 73 kDa (UL[-1]), which both are predominantly localized in the nuclei of virus infected chicken cells. In summary, our results indicate that duplication of a spliced ILTV-specific gene encoding a nuclear protein has occurred during evolution of ILTV.
Figures

References
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Bagust T J, Guy J S. Laryngotracheitis. In: Calnek B W, Barnes H J, Beard C W, McDougald L R, Saif Y M, editors. Diseases of poultry. 10th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press; 1997. pp. 527–539.
-
- Ben-Porat T, Veach R A, Ihara S. Localization of the regions of homology between the genomes of herpes simplex virus type 1 and pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1983;127:194–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

