Serine and threonine phosphorylation of the paxillin LIM domains regulates paxillin focal adhesion localization and cell adhesion to fibronectin
- PMID: 9658172
- PMCID: PMC25420
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.7.1803
Serine and threonine phosphorylation of the paxillin LIM domains regulates paxillin focal adhesion localization and cell adhesion to fibronectin
Abstract
We have previously shown that the LIM domains of paxillin operate as the focal adhesion (FA)-targeting motif of this protein. In the current study, we have identified the capacity of paxillin LIM2 and LIM3 to serve as binding sites for, and substrates of serine/threonine kinases. The activities of the LIM2- and LIM3-associated kinases were stimulated after adhesion of CHO.K1 cells to fibronectin; consequently, a role for LIM domain phosphorylation in regulating the subcellular localization of paxillin after adhesion to fibronectin was investigated. An avian paxillin-CHO.K1 model system was used to explore the role of paxillin phosphorylation in paxillin localization to FAs. We found that mutations of paxillin that mimicked LIM domain phosphorylation accelerated fibronectin-induced localization of paxillin to focal contacts. Further, blocking phosphorylation of the LIM domains reduced cell adhesion to fibronectin, whereas constitutive LIM domain phosphorylation significantly increased the capacity of cells to adhere to fibronectin. The potentiation of FA targeting and cell adhesion to fibronectin was specific to LIM domain phosphorylation as mutation of the amino-terminal tyrosine and serine residues of paxillin that are phosphorylated in response to fibronectin adhesion had no effect on the rate of FA localization or cell adhesion. This represents the first demonstration of the regulation of protein localization through LIM domain phosphorylation and suggests a novel mechanism of regulating LIM domain function. Additionally, these results provide the first evidence that paxillin contributes to "inside-out" integrin-mediated signal transduction.
Figures
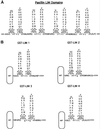



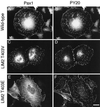
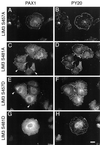



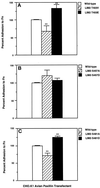
References
-
- Arber S, Caroni P. Specificity of single LIM motifs in targeting and LIM/LIM interactions in situ. Genes Dev. 1996;10:289–300. - PubMed
-
- Aznavoorian S, Stracke ML, Parsons J, McClanahan J, Liotta LA. Integrin αvβ3 mediates chemotactic and haptotactic motility in human melanoma cells through different signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:3247–3254. - PubMed
-
- Barreuther MF, Grabel LB. The role of phosphorylation in modulating β1 integrin localization. Exp Cell Res. 1996;222:10–15. - PubMed
-
- Bellis SL, Miller JT, Turner CE. Characterization of tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin in vitro by focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:17437–17441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

