Spontaneous secretion of interferon gamma and interleukin 4 by human intraepithelial and lamina propria gut lymphocytes
- PMID: 9659157
- PMCID: PMC1727108
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.42.5.643
Spontaneous secretion of interferon gamma and interleukin 4 by human intraepithelial and lamina propria gut lymphocytes
Abstract
Background: Cytokines secreted by intestinal T lymphocytes probably play a critical role in regulation of the gut associated immune responses.
Aims: To quantify interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) and interleukin 4 (IL-4) secreting cells (SC) among human intraepithelial (IEL) and lamina propria (LPL) lymphocytes from the duodenum and right colon in non-pathological situations and in the absence of in vitro stimulation.
Patients: Duodenal and right colonic biopsy specimens were obtained from patients with no inflammation of the intestinal mucosa.
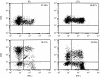
Methods: Intraepithelial and lamina propria cell suspensions were assayed for numbers of cells spontaneously secreting IFN-gamma and IL-4 by a two site reverse enzyme linked immunospot technique (ELISPOT).
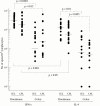
Results: The relatively high proportion of duodenal lymphocytes spontaneously secreting IFN-gamma (IEL 3.6%; LPL 1.9%) and IL-4 (IEL 1.3%; LPL 0.7%) contrasted with the very low numbers of spontaneously IFN-gamma SC and the absence of spontaneously IL-4 SC among peripheral blood mononuclear cells. In the basal state, both IFN-gamma and IL-4 were mainly produced by CD4+ cells. Within the colon, only 0.2% of IEL and LPL secreted IFN-gamma in the basal state, and 0.1% secreted IL-4.
Conclusions: Compared with peripheral lymphocytes substantial proportions of intestinal epithelial and lamina propria lymphocytes spontaneously secrete IFN-gamma and/or IL-4. These cytokines are probably involved in the normal homoeostasis of the human intestinal mucosa. Disturbances in their secretion could play a role in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal diseases.
Figures
Comment in
-
Just how inflamed is the normal gut?Gut. 1998 May;42(5):603-4. doi: 10.1136/gut.42.5.603. Gut. 1998. PMID: 9659148 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
