Evidence for altered hepatic matrix degradation in genetic haemochromatosis
- PMID: 9659170
- PMCID: PMC1727107
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.42.5.715
Evidence for altered hepatic matrix degradation in genetic haemochromatosis
Abstract
Background: Altered matrix degradation contributes to fibrosis in some liver diseases but the role of matrix degradation in fibrogenesis associated with genetic haemochromatosis has not previously been addressed.
Aims: To measure serum concentrations of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP), MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-3 in patients with haemochromatosis and control subjects.
Patients: Forty patients with haemochromatosis and 19 healthy control subjects. Ten of the 40 patients were studied before and after venesection therapy.
Methods: Serum levels of TIMP-1, MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-3 were measured by enzyme immunoassay and correlated to hepatic iron concentration and degree of histological fibrosis.
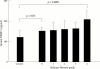
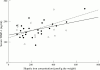
Results: Serum TIMP-1 was increased in patients with haemochromatosis compared with controls (163 (30) versus 123 (28) ng/ml, p < 0.0002). Mean serum TIMP-1 concentration of patients with haemochromatosis without fibrosis was significantly higher than in controls (153 (16) versus 123 (28) ng/ml, p = 0.03). Serum TIMP-1 concentration correlated with both hepatic iron concentration and hepatic iron index (r = 0.42, p < 0.01; r = 0.42, p < 0.01). Serum MMP-2 concentrations correlated with increasing degree of fibrosis in patients with haemochromatosis (r = 0.38, p = 0.01). The mean MMP-1: TIMP-1, MMP-2:TIMP-1 and age/sex matched MMP-3:TIMP-1 ratios were significantly lower in patients with haemochromatosis than controls (0.11 (0.06) versus 0.2 (0.14), p = 0.02; 3.32 (0.9) versus 3.91 (0.81), p = 0.05; and 0.26 (0.12) versus 0.47 (0.27), p = 0.007, respectively). Following venesection, MMP-2 and MMP-3 concentrations increased by 11% (p = 0.03) and 19% (p = 0.03), respectively.
Conclusions: This study provides the first evidence of an alteration in matrix degradation in haemochromatosis that may be a contributing factor to hepatic fibrogenesis in this disease.
Figures
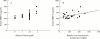
Similar articles
-
Elevated serum type IV collagen: a sensitive indicator of the presence of cirrhosis in haemochromatosis.J Hepatol. 1999 Jul;31(1):47-52. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(99)80162-7. J Hepatol. 1999. PMID: 10424282
-
Circulating matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 as serum markers of fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Relationship to interferon response.J Hepatol. 1997 Mar;26(3):574-83. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80423-0. J Hepatol. 1997. PMID: 9075665
-
Circulating matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, 9 and their inhibitors TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 as serum markers of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C: comparison with PIIINP and hyaluronic acid.Am J Gastroenterol. 2004 Feb;99(2):271-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04055.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15046217
-
Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors.Anticancer Res. 1999 Mar-Apr;19(2C):1589-92. Anticancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10365151 Review.
-
New insights into fibrosis from the ECM degradation perspective: the macrophage-MMP-ECM interaction.Cell Biosci. 2022 Jul 27;12(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00856-w. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35897082 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hereditary hemochromatosis in the post-HFE era.Hepatology. 2008 Sep;48(3):991-1001. doi: 10.1002/hep.22507. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18752323 Free PMC article.
-
Paediatric cholestatic liver disease: Diagnosis, assessment of disease progression and mechanisms of fibrogenesis.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2010 Jun 15;1(2):69-84. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v1.i2.69. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2010. PMID: 21607144 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of hepatic iron concentration reduction on hepatic fibrosis and damage in rats with cholestatic liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jan 14;12(2):240-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.240. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16482624 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the prophylactic effect of silymarin and deferoxamine on iron overload-induced hepatotoxicity in rat.J Med Toxicol. 2010 Mar;6(1):22-6. doi: 10.1007/s13181-010-0030-9. J Med Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20182837 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
