Distribution of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein at the apical surface of MDCK cells examined at a resolution of <100 A using imaging fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- PMID: 9660864
- PMCID: PMC2133040
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.1.69
Distribution of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein at the apical surface of MDCK cells examined at a resolution of <100 A using imaging fluorescence resonance energy transfer
Erratum in
- J Cell Biol 1998 Aug 10;142(3):following 881
Abstract
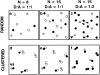
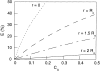
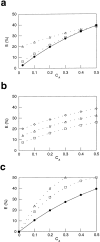
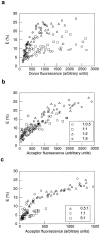
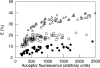
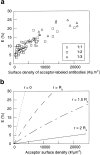
Membrane microdomains ("lipid rafts") enriched in glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins, glycosphingolipids, and cholesterol have been implicated in events ranging from membrane trafficking to signal transduction. Although there is biochemical evidence for such membrane microdomains, they have not been visualized by light or electron microscopy. To probe for microdomains enriched in GPI- anchored proteins in intact cell membranes, we used a novel form of digital microscopy, imaging fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), which extends the resolution of fluorescence microscopy to the molecular level (<100 A). We detected significant energy transfer between donor- and acceptor-labeled antibodies against the GPI-anchored protein 5' nucleotidase (5' NT) at the apical membrane of MDCK cells. The efficiency of energy transfer correlated strongly with the surface density of the acceptor-labeled antibody. The FRET data conformed to theoretical predictions for two-dimensional FRET between randomly distributed molecules and were inconsistent with a model in which 5' NT is constitutively clustered. Though we cannot completely exclude the possibility that some 5' NT is in clusters, the data imply that most 5' NT molecules are randomly distributed across the apical surface of MDCK cells. These findings constrain current models for lipid rafts and the membrane organization of GPI-anchored proteins.
Figures





Similar articles
-
High-resolution FRET microscopy of cholera toxin B-subunit and GPI-anchored proteins in cell plasma membranes.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 May;11(5):1645-55. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.5.1645. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10793141 Free PMC article.
-
VIP21/caveolin, glycosphingolipid clusters and the sorting of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in epithelial cells.EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):42-53. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06233.x. EMBO J. 1994. PMID: 8306971 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored 5'-nucleotidase CD73 from adiposomes into rat adipocytes stimulates lipid synthesis.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;160(4):878-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00724.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20590586 Free PMC article.
-
GPI-anchored protein organization and dynamics at the cell surface.J Lipid Res. 2016 Feb;57(2):159-75. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R062885. Epub 2015 Sep 22. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 26394904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detergent-resistant membrane microdomains and apical sorting of GPI-anchored proteins in polarized epithelial cells.Int J Med Microbiol. 2002 Feb;291(6-7):439-45. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00151. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11890542 Review.
Cited by
-
Different cell surface oligomeric states of B7-1 and B7-2: implications for signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Oct 25;102(43):15569-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507257102. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16221763 Free PMC article.
-
Why are lipid rafts not observed in vivo?Biophys J. 2007 Nov 1;93(9):3113-9. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.101931. Epub 2007 Jul 27. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17660324 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic, yet structured: The cell membrane three decades after the Singer-Nicolson model.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 8;100(14):8053-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1332550100. Epub 2003 Jun 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12832616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probing novel GPCR interactions using a combination of FRET and TIRF.Commun Integr Biol. 2010 Jul;3(4):343-6. doi: 10.4161/cib.3.4.11764. Commun Integr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20798821 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral diffusion coefficients in membranes measured by resonance energy transfer and a new algorithm for diffusion in two dimensions.Biophys J. 2002 Mar;82(3):1358-72. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75491-X. Biophys J. 2002. PMID: 11867452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adair BD, Engelman DM. Glycophorin A helical transmembrane domains dimerize in phospholipid bilayers: a resonance energy transfer study. Biochemistry. 1994;33:5539–5544. - PubMed
-
- Adams SR, Harootunian AT, Buechler YJ, Taylor SS, Tsien RY. Fluorescence ratio imaging of cyclic AMP in single cells. Nature. 1991;349:694–697. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed SN, Brown DA, London E. On the origin of sphingolipid/ cholesterol-rich detergent-insoluble cell membranes: physiological concentrations of cholesterol and sphingolipid induce formation of a detergent- insoluble, liquid-ordered lipid phase in model membranes. Biochemistry. 1997;36:10944–10953. - PubMed
-
- Arreaza G, Melkonian KA, LaFevre-Bernt M, Brown DA. Triton X-100-resistant membrane complexes from cultured kidney epithelial cells contain the Src family protein tyrosine kinase p62yes. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:19123–19127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

