Human CASK/LIN-2 binds syndecan-2 and protein 4.1 and localizes to the basolateral membrane of epithelial cells
- PMID: 9660868
- PMCID: PMC2133028
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.1.129
Human CASK/LIN-2 binds syndecan-2 and protein 4.1 and localizes to the basolateral membrane of epithelial cells
Erratum in
- J Cell Biol 1998 Aug 24;142(4):following 1156. Wood DF [corrected to Woods DF]
Abstract
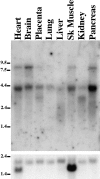
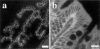
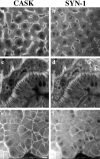
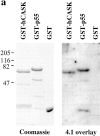
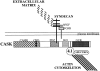
In Caenorhabditis elegans, mutations in the lin-2 gene inactivate the LET-23 receptor tyrosine kinase/Ras/MAP kinase pathway required for vulval cell differentiation. One function of LIN-2 is to localize LET-23 to the basal membrane domain of vulval precursor cells. LIN-2 belongs to the membrane-associated guanylate kinase family of proteins. We have cloned and characterized the human homolog of LIN-2, termed hCASK, and Northern and Western blot analyses reveal that it is ubiquitously expressed. Indirect immunofluorescence localizes CASK to distinct lateral and/or basal plasma membrane domains in different epithelial cell types. We detect in a yeast two-hybrid screen that the PDZ domain of hCASK binds to the heparan sulfate proteoglycan syndecan-2. This interaction is confirmed using in vitro binding assays and immunofluorescent colocalization. Furthermore, we demonstrate that hCASK binds the actin-binding protein 4.1. Syndecans are known to bind extracellular matrix, and to form coreceptor complexes with receptor tyrosine kinases. We speculate that CASK mediates a link between the extracellular matrix and the actin cytoskeleton via its interaction with syndecan and with protein 4.1. Like other membrane-associated guanylate kinases, its multidomain structure enables it to act as a scaffold at the membrane, potentially recruiting multiple proteins and coordinating signal transduction.
Figures
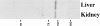

References
-
- Aroia RV, Koga M, Mendel JE, Ohshima Y, Sternberg PW. The let-23 gene necessary for Caenorhabditis elegansvulval induction encodes a tyrosine kinase of the EGF receptor subfamily. Nature. 1990;348:693–699. - PubMed
-
- Balda MS, Anderson JM, Matter K. The SH3 domain of the tight junction protein ZO-1 binds to a serine protein kinase that phosphorylates a region COOH-terminal to this domain. FEBS Lett. 1996;399:326–332. - PubMed
-
- Bernfield M, Kokenyesi R, Kato M, Hinkes MT, Spring J, Gallo RL, Lose EJ. Biology of the syndecans: a family of transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Ann Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:365–393. - PubMed
-
- Braun AP, Schulman H. The multifunctional calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase: from form to function. Ann Rev Physiol. 1995;57:417–445. - PubMed
-
- Brenman JE, Chao DS, Gee SH, McGee AW, Craven SE, Santillano DR, Wu Z, Huang F, Xia H, Peters MF, Froehner SC, Bredt DS. Interaction of nitric oxide Synthase with the postsynaptic density protein PSD95 and α1-syntrophin mediated by PDZ domains. Cell. 1996a;84:757–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

