Dual actions of sphingosine-1-phosphate: extracellular through the Gi-coupled receptor Edg-1 and intracellular to regulate proliferation and survival
- PMID: 9660876
- PMCID: PMC2133030
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.1.229
Dual actions of sphingosine-1-phosphate: extracellular through the Gi-coupled receptor Edg-1 and intracellular to regulate proliferation and survival
Abstract
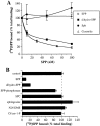
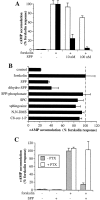
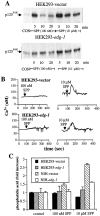
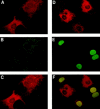
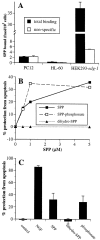
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (SPP), a bioactive lipid, acts both intracellularly and extracellularly to cause pleiotropic biological responses. Recently, we identified SPP as a ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Edg-1 (Lee, M.-J., J.R. Van Brocklyn, S. Thangada, C.H. Liu, A.R. Hand, R. Menzeleev, S. Spiegel, and T. Hla. 1998. Science. 279:1552-1555). Edg-1 binds SPP with remarkable specificity as only sphinganine-1-phosphate displaced radiolabeled SPP, while other sphingolipids did not. Binding of SPP to Edg-1 resulted in inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation, in a pertussis toxin-sensitive manner. In contrast, two well-characterized biological responses of SPP, mitogenesis and prevention of apoptosis, were clearly unrelated to binding to Edg-1 and correlated with intracellular uptake. SPP also stimulated signal transduction pathways, including calcium mobilization, activation of phospholipase D, and tyrosine phosphorylation of p125(FAK), independently of edg-1 expression. Moreover, DNA synthesis in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts was significantly and specifically increased by microinjection of SPP. Finally, SPP suppresses apoptosis of HL-60 and pheochromocytoma PC12 cells, which do not have specific SPP binding or expression of Edg-1 mRNA. Conversely, sphinganine-1-phosphate, which binds to and signals via Edg-1, does not have any significant cytoprotective effect. Thus, SPP is a prototype for a novel class of lipid mediators that act both extracellularly as ligands for cell surface receptors and intracellularly as second messengers.
Figures



References
-
- An S, Bleu T, Huang W, Hallmark OG, Coughling SR, Goetzel EJ. Identification of cDNAs encoding two G protein-coupled receptors for lysosphingolipids. FEBS Lett. 1997;417:279–282. - PubMed
-
- Blakesly VA, Beitner-Johnson D, Van Brocklyn JR, Rani S, Shen-Orr Z, Stannard BS, Spiegel S, LeRoith D. Sphingosine 1-phosphate stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of Crk. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:16211–16215. - PubMed
-
- Bornfeldt KE, Graves LM, Raines EW, Igarashi Y, Wayman G, Yamamura S, Yatomi Y, Sidhu JS, Krebs EG, Hakomori S, Ross R. Sphingosine-1-phosphate inhibits PDGF-induced chemotaxis of human arterial smooth muscle cells: spatial and temporal modulation of PDGF chemotactic signal transduction. J Cell Biol. 1995;130:193–206. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buehrer BM, Bardes ES, Bell RM. Protein kinase C-dependent regulation of human erythroleukemia (HEL) cell sphingosine kinase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1303:233–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

