Hyperpolarization-activated cationic currents (Ih) in neurones of the trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus of the rat
- PMID: 9660886
- PMCID: PMC2231081
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.00695.x
Hyperpolarization-activated cationic currents (Ih) in neurones of the trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus of the rat
Abstract
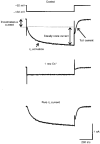
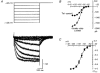
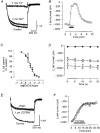
1. We studied the voltage-dependent current activated by membrane hyperpolarization in sensory proprioceptive trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus (MNV) neurones. 2. Membrane hyperpolarization (from -62 to -132 mV in 10 mV steps) activated slowly activating and non-inactivating inward currents. The hyperpolarization-activated currents could be described by activation curves with a half-maximal activation potential (V ) of -93 mV, slope (k) of 8.4 mV, and maximally activated currents (Imax) of around 1 nA. The reversal potential of the hyperpolarization-activated currents was -57 mV. 3. Extracellular Cs+ blocked hyperpolarization-activated currents rapidly and reversibly in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 of 100 microM and Hill slope of 0.8. ZD7288 (1 microM; 4-(N-ethyl-N-phenylamino)-1,2-dimethyl-6-(methylamino) pyridinium chloride), the compound developed as an inhibitor of the cardiac hyperpolarization-activated current (If), also blocked the hyperpolarization-activated currents in MNV neurones. Extracellular Ba2+ (1 mM) did not affect hyperpolarization-activated currents. We tested whether the hyperpolarization-activated currents contribute to the somatic membrane properties of MNV neurones by performing some experiments using current-clamp recording. In such experiments application of Cs+ (1 mM) produced no effect on neuronal resting membrane potentials. 4. During the course of our experiments we noticed that activating ATP-gated non-selective cation channels (P2X receptors) caused an inhibition of Ih associated with a V shift of 10 mV in the hyperpolarizing direction. This P2X receptor-mediated inhibition of Ih was blocked in recordings made with the rapid calcium chelator BAPTA (11 mM) in the pipette solution. 5. We conclude that the current activated by membrane hyperpolarization in MNV neurones is Ih on the basis of its similarity to Ih observed in other neuronal preparations. Activation of Ih can account for the anomalous time-dependent inward rectification that has previously been described in MNV neurones.
Figures
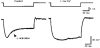

Similar articles
-
ATP-gated cation channels (P2X purinoceptors) in trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus neurons of the rat.J Physiol. 1997 Feb 1;498 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):709-15. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp021895. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9051582 Free PMC article.
-
On the nature of anomalous rectification in thalamocortical neurones of the cat ventrobasal thalamus in vitro.J Physiol. 1997 Dec 15;505 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):727-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.727ba.x. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9457648 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of block by ZD 7288 of the hyperpolarization-activated inward rectifying current in guinea pig substantia nigra neurons in vitro.J Neurophysiol. 1995 Dec;74(6):2366-78. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.74.6.2366. J Neurophysiol. 1995. PMID: 8747199
-
Properties of native P2X receptors in rat trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus neurones: lack of correlation with known, heterologously expressed P2X receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2001;40(1):96-105. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(00)00108-8. Neuropharmacology. 2001. PMID: 11077075
-
Properties of a hyperpolarization-activated cation current and its role in rhythmic oscillation in thalamic relay neurones.J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:291-318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018331. J Physiol. 1990. PMID: 1712843 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic perturbations suggest a role of the resting potential in regulating the expression of the ion channels of the KCNA and HCN families in octopus cells of the ventral cochlear nucleus.Hear Res. 2017 Mar;345:57-68. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Hear Res. 2017. PMID: 28065805 Free PMC article.
-
Kappa-opioid receptor-mediated enhancement of the hyperpolarization-activated current (I(h)) through mobilization of intracellular calcium in rat nucleus raphe magnus.J Physiol. 2003 May 1;548(Pt 3):765-75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.037622. Epub 2003 Mar 21. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12651920 Free PMC article.
-
Blockage of HCN Channels Inhibits the Function of P2X Receptors in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons.Neurochem Res. 2022 Apr;47(4):1083-1096. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03509-5. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35064517
-
Cholinergic control of excitability of spinal motoneurones in the salamander.J Physiol. 2006 Feb 1;570(Pt 3):525-40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.098970. Epub 2005 Nov 24. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16308350 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric control of gating and kinetics at P2X(4) receptor channels.J Neurosci. 1999 Sep 1;19(17):7289-99. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-17-07289.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10460235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aantaa R, Marjamaki A, Scheinin M. Molecular pharmacology of alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes. Annals of Medicine. 1995;27:439–449. - PubMed
-
- Banks MI, Pearce RA, Smith PH. Hyperpolarisation-activated cation current (IH) in neurones of the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body: voltage clamp analysis and enhancement by norepinephrine and cAMP suggest a modulatory mechanism in the auditory brain stem. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1993;70:1420–1432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

