Inhibition of oxidative metabolism increases persistent sodium current in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 9660889
- PMCID: PMC2231084
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.735bj.x
Inhibition of oxidative metabolism increases persistent sodium current in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons
Abstract
1. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from freshly dissociated rat CA1 neurons revealed a large transient Na+ current (INa,T) and a smaller, inactivation-resistant persistent Na+ current (INa,P). Both currents could be blocked with TTX. 2. The average current densities of INa,T and INa,P in thirty cells were 111.0 +/- 9.62 and 0.87 +/- 0.13 pA pF-1, respectively. 3. Inhibiting oxidative phosphorylation by adding 5 mM sodium cyanide to the pipette solution significantly increased the amplitude of INa,P but had no significant effect on the amplitude of INa,T. 4. Exposing CA1 neurons to hypoxia for more than 7 min caused an increase in the amplitude of INa,P. There was also a delayed decrease in the amplitude of INa,T. 5. INa,P was more sensitive to the Na+ channel blockers TTX and lidocaine than INa,T. The IC50 for the effect of TTX on INa,P was 9.1 +/- 1.2 nM whereas the IC50 for INa,T was 37.1 +/- 1.2 nM, approximately 4-fold higher. Lidocaine (lignocaine; 1 microM) reduced INa,P to 0.24 +/- 0.15 of control (n = 4) whereas INa,T was essentially unaffected (0.99 +/- 0. 11, n = 4). 6. These results show that INa,P is increased when oxidative metabolism is blocked in CA1 neurons. The persistent influx of Na+ through non-inactivating Na+ channels can be blocked by concentrations of Na+ channel blockers that do not affect INa,T.
Figures


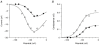

 ) and persistent (▪) Na+ current. The bars show the average normalized amplitude of the current and the vertical lines denote 1
) and persistent (▪) Na+ current. The bars show the average normalized amplitude of the current and the vertical lines denote 1 Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide increases persistent sodium current in rat hippocampal neurons.J Physiol. 1999 Oct 15;520 Pt 2(Pt 2):451-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.t01-1-00451.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10523414 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of metabolic inhibition on the excitability of isolated hippocampal CA1 neurons: developmental aspects.J Neurophysiol. 1991 Nov;66(5):1471-82. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.5.1471. J Neurophysiol. 1991. PMID: 1662712
-
Oxygen-sensing persistent sodium channels in rat hippocampus.J Physiol. 2000 Nov 15;529 Pt 1(Pt 1):107-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00107.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11080255 Free PMC article.
-
PGE2 modulates the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium current in neonatal rat dorsal root ganglion neurones via the cyclic AMP-protein kinase A cascade.J Physiol. 1996 Sep 1;495 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):429-40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021604. J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8887754 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-dependent conductances of solitary ganglion cells dissociated from the rat retina.J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:361-91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016497. J Physiol. 1987. PMID: 2443669 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Persistent sodium current in layer 5 neocortical neurons is primarily generated in the proximal axon.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 29;26(13):3465-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4907-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16571753 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent sodium currents in neurons: potential mechanisms and pharmacological blockers.Pflugers Arch. 2024 Oct;476(10):1445-1473. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-02980-7. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Pflugers Arch. 2024. PMID: 38967655 Free PMC article.
-
Optical and pharmacological tools to investigate the role of mitochondria during oxidative stress and neurodegeneration.Prog Neurobiol. 2006 Jun;79(3):136-71. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2006.07.001. Prog Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16920246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of mitochondrial inhibition on excitability and cytosolic Ca2+ levels in brainstem motoneurones from mouse.J Physiol. 2004 Feb 15;555(Pt 1):45-59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.053900. Epub 2003 Dec 5. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14660707 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Sodium Current Mediates the Steep Voltage Dependence of Spatial Coding in Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons.Neuron. 2018 Jul 11;99(1):147-162.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.05.025. Epub 2018 Jun 14. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 29909995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonzo A, Llinás RR. Subthreshold Na+-dependent theta-like rythmicity in stellate cells of entorhinal cortex layer II. Nature. 1989;342:1175–1177. - PubMed
-
- Amitai Y. Membrane potential oscillations underlying firing patterns in neocortical neurons. Neuroscience. 1994;63:151–161. 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90013-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bickler PE, Hansen BM. Causes of calcium accumulation in rat cortical brain slices during hypoxia and ischaemia: role of ion channels and membrane damage. Brain Research. 1994;665:269–276. - PubMed
-
- Crill WE. Persistent sodium currents in mammalian central neurons. Annual Review of Physiology. 1996;58:349–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

