Changes in Achilles tendon moment arm from rest to maximum isometric plantarflexion: in vivo observations in man
- PMID: 9660906
- PMCID: PMC2231068
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.977bj.x
Changes in Achilles tendon moment arm from rest to maximum isometric plantarflexion: in vivo observations in man
Abstract
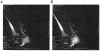
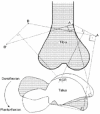
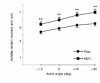
1. The purpose of the present study was to examine the effect of a plantarflexor maximum voluntary contraction (MVC) on Achilles tendon moment arm length. 2. Sagittal magnetic resonance (MR) images of the right ankle were taken in six subjects both at rest and during a plantarflexor MVC in the supine position at a knee angle of 90 deg and at ankle angles of -30 deg (dorsiflexed direction), -15 deg, 0 deg (neutral ankle position), +15 deg (plantarflexed direction), +30 deg and +45 deg. A system of mechanical stops, support triangles and velcro straps was used to secure the subject in the above positions. Location of a moving centre of rotation was calculated for ankle rotations from -30 to 0 deg, -15 to +15 deg, 0 to +30 deg and +15 to +45 deg. All instant centres of rotation were calculated both at rest and during MVC. Achilles tendon moment arms were measured at ankle angles of -15, 0, +15 and +30 deg. 3. At any given ankle angle, Achilles tendon moment arm length during MVC increased by 1-1.5 cm (22-27 %, P < 0.01) compared with rest. This was attributed to a displacement of both Achilles tendon by 0.6-1.1 cm (P < 0.01) and all instant centres of rotation by about 0.3 cm (P < 0.05) away from their corresponding resting positions. 4. The findings of this study have important implications for estimating loads in the musculoskeletal system. Substantially unrealistic Achilles tendon forces and moments generated around the ankle joint during a plantarflexor MVC would be calculated using resting Achilles tendon moment arm measurements.
Figures
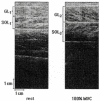
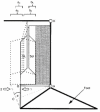
References
-
- An KN, Hui FC, Morrey BF, Linscheid RL, Chao EY. Muscles across the elbow joint: a biomechanical analysis. Journal of Biomechanics. 1981;14:659–669. 10.1016/0021-9290(81)90048-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burdett RG. Forces predicted at the ankle during running. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 1982;14:308–316. - PubMed
-
- Cummins EJ, Anson BJ, Carr BW, Wright RR, Hauser EDW. The structure of calcaneal tendon in relation to orthopedic surgery. Surgery, Gynecology and Obstetrics. 1946;83:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Fukunaga T, Roy RR, Shellock FG, Hodson JA, Edgerton VR. Specific tension of human plantarflexors and dorsiflexors. Journal of Applied Physiology. 1996;80:158–165. - PubMed
-
- Kawakami Y, Nakazawa K, Fujimoto T, Nozaki D, Miyashita M, Fukunaga T. Specific tension of elbow flexor and extensor muscles based on magnetic resonance imaging. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 1994;68:139–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

