Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants isolated from AIDS patients after prolonged adefovir dipivoxil therapy
- PMID: 9660994
- PMCID: PMC105656
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.7.1620
Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants isolated from AIDS patients after prolonged adefovir dipivoxil therapy
Abstract
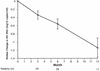
Adefovir dipivoxil [bis(pivaloyloxymethyl)-ester prodrug], an orally bioavailable prodrug of adefovir [9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine], is currently in phase III clinical trials for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). In vitro experiments demonstrated that either a K65R or a K70E mutation in HIV reverse transcriptase (RT) was selected in the presence of adefovir, conferring a 16- or 9-fold decrease in susceptibility to adefovir, respectively. Previous data demonstrated that patients receiving adefovir dipivoxil monotherapy (125 mg daily) for 12 weeks experienced a median decrease in HIV RNA levels of 0.5 log10 copies/ml and that resistance to adefovir dipivoxil did not arise during that period. In the present investigation, a further study was undertaken to investigate whether RT mutations developed among viruses from patients who completed the 12-week study and who opted to enroll in a maintenance phase of prolonged (6- to 12-month) adefovir dipivoxil therapy (120 mg daily). Concomitant treatment with antiretroviral agents was permitted during the maintenance phase. The median decreases in HIV RNA levels for patients who completed 6 or 12 months of maintenance-phase dosing were 0.6 and 1.14 log10 copies/ml, respectively. The reductions in the HIV RNA levels were similar among patients who received adefovir dipivoxil with or without concomitant treatment with antiretroviral agents. Viruses from 8 of 29 patients dosed for up to 12 months developed RT mutations that were not present at baseline; these mutations may have been related to adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Viruses from two of the eight patients developed the K70E mutation while the patients were on therapy, but none of the viruses from patients developed the K65R RT substitution. Despite the development of RT mutations, sustained reductions (6 to 12 months) in viral load (> or = 0.7 log10 copies/ml decrease from baseline) were observed in all eight patients.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adefovir dipivoxil.Drugs. 1999 Sep;58(3):479-87; discussion 488-9. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199958030-00010. Drugs. 1999. PMID: 10493275 Review.
-
Adefovir and tenofovir susceptibilities of HIV-1 after 24 to 48 weeks of adefovir dipivoxil therapy: genotypic and phenotypic analyses of study GS-96-408.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2001 Aug 15;27(5):450-8. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200108150-00005. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2001. PMID: 11511821 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of adefovir dipivoxil with antiretroviral therapy: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 1999 Dec 22-29;282(24):2305-12. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.24.2305. JAMA. 1999. PMID: 10612317 Clinical Trial.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase expressing the K70E mutation exhibits a decrease in specific activity and processivity.Mol Pharmacol. 1998 Aug;54(2):291-7. doi: 10.1124/mol.54.2.291. Mol Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9687570
-
Adefovir dipivoxil: a review of its use in chronic hepatitis B.Drugs. 2003;63(20):2215-34. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363200-00007. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 14498759 Review.
Cited by
-
9-[2-(Phosphonomethoxy)propyl]adenine (PMPA) therapy prolongs survival of infant macaques inoculated with simian immunodeficiency virus with reduced susceptibility to PMPA.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999 Apr;43(4):802-12. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.4.802. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999. PMID: 10103184 Free PMC article.
-
Novel drug resistance pattern associated with the mutations K70G and M184V in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Dec;51(12):4489-91. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00687-07. Epub 2007 Sep 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17876005 Free PMC article.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil.Drugs. 1999 Sep;58(3):479-87; discussion 488-9. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199958030-00010. Drugs. 1999. PMID: 10493275 Review.
-
Sequential emergence and clinical implications of viral mutants with K70E and K65R mutation in reverse transcriptase during prolonged tenofovir monotherapy in rhesus macaques with chronic RT-SHIV infection.Retrovirology. 2007 Apr 6;4:25. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-4-25. Retrovirology. 2007. PMID: 17417971 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretroviral Drug Resistance in HIV-1.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 1999 Aug;1(3):289-297. doi: 10.1007/s11908-999-0032-4. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 1999. PMID: 11095801
References
-
- Balzarini J, De Clercq E. 5-Phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate synthetase converts the acyclic nucleoside phosphonates 9-(3-hydroxy-2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine and 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine directly to their antivirally active diphosphate derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:8686–8689. - PubMed
-
- Balzarini J, Perno C F, Schols D, De Clercq E. Activity of acyclic nucleoside phosphonate analogues against human immunodeficiency virus in monocyte/macrophages and peripheral blood lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;178:329–335. - PubMed
-
- Balzarini J, Holy A, Jindrich J, Naesens L, Snoeck R, Schols D, De Clercq E. Differential antiherpesvirus and antiretrovirus effects of the (S) and (R) enantiomers of acyclic nucleoside phosphonates: potent and selective in vitro and in vivo antiretrovirus activities of (R)-9-(2-phosphonomethoxypropyl) derivatives of adenine and 2,6-diaminopurine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37:332–338. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balzarini J, Nave J F, Becker M A, Tatiban M, DeClercq E. Kinetic properties of adenine nucleotide analogues against purified 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate synthetases from E. coli, rat liver, and human erythrocytes. Nucleosides Nucleotides. 1995;14:1861–1871.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

