Antiviral activity of a selective ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor against acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus type 1 in vivo
- PMID: 9660995
- PMCID: PMC105657
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.7.1629
Antiviral activity of a selective ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor against acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus type 1 in vivo
Abstract
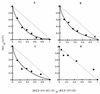
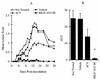
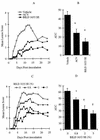
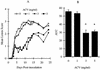
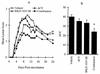
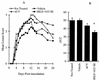
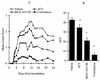
The present study reports the activity of BILD 1633 SE against acyclovir (ACV)-resistant herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections in athymic nude (nu/nu) mice. BILD 1633 SE is a novel peptidomimetic inhibitor of HSV ribonucleotide reductase (RR). In vitro, it is more potent than ACV against several strains of wild-type as well as ACV-resistant HSV mutants. Its in vivo activity was tested against cutaneous viral infections in athymic nude mice infected with the ACV-resistant isolates HSV type 1 (HSV-1) dlsptk and PAAr5, which contain mutations in the viral thymidine kinase gene and the polymerase gene, respectively. Following cutaneous infection of athymic nude mice, both HSV-1 dlsptk and PAAr5 induced significant, reproducible, and persistent cutaneous lesions that lasted for more than 2 weeks. A 10-day treatment regimen with ACV given topically four times a day as a 5% cream or orally at up to 5 mg/ml in drinking water was partially effective against HSV-1 PAAr5 infection with a reduction of the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of 34 to 48%. The effects of ACV against HSV-1 dlsptk infection were not significant when it was administered topically and were only marginal when it was given in drinking water. Treatment under identical conditions with 5% topical BILD 1633 SE significantly reduced the cutaneous lesions caused by both HSV-1 dlsptk and PAAr5 infections. The effect of BILD 1633 SE against HSV-1 PAAr5 infections was more prominent and was inoculum and dose dependent, with AUC reductions of 96 and 67% against infections with 10(6) and 10(7) PFU per inoculation site, respectively. BILD 1633 SE also significantly decreased the lesions caused by HSV-1 dlsptk infection (28 to 51% AUC reduction). Combination therapy with topical BILD 1633 SE (5%) and ACV in drinking water (5 mg/ml) produced an antiviral effect against HSV-1 dlsptk and PAAr5 infections that was more than the sum of the effects of both drugs. This is the first report that a selective HSV RR subunit association inhibitor can be effective against ACV-resistant HSV infections in vivo.
Figures
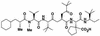
Similar articles
-
Oral bioavailability and in vivo efficacy of the helicase-primase inhibitor BILS 45 BS against acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus type 1.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Jun;47(6):1798-804. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.6.1798-1804.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12760851 Free PMC article.
-
The antiviral activity of the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor BILD 1351 SE in combination with acyclovir against HSV type-1 in cell culture.Antiviral Res. 1998 Jul;39(1):35-46. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(98)00028-x. Antiviral Res. 1998. PMID: 9754948
-
Inactivators of herpes simplex virus ribonucleotide reductase: hematological profiles and in vivo potentiation of the antiviral activity of acyclovir.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):934-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.36.5.934. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992. PMID: 1324641 Free PMC article.
-
Potential for combined therapy with 348U87, a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor, and acyclovir as treatment for acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus infection.J Med Virol. 1993;Suppl 1:146-9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890410528. J Med Virol. 1993. PMID: 8245882 Review.
-
[Development of antiviral therapeutic agents from traditional medicines].Yakugaku Zasshi. 1998 Sep;118(9):383-400. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.118.9_383. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1998. PMID: 9778999 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Oral bioavailability and in vivo efficacy of the helicase-primase inhibitor BILS 45 BS against acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus type 1.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Jun;47(6):1798-804. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.6.1798-1804.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12760851 Free PMC article.
-
Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors hydroxyurea, didox, and trimidox inhibit human cytomegalovirus replication in vitro and synergize with ganciclovir.Antiviral Res. 2013 Oct;100(1):151-8. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23933116 Free PMC article.
-
Lithocholic Acid Oleate Preparative Synthesis and Its Formulation with Lithocholic Acid as a Preventive Antiviral: In Vitro and In Vivo Assays Against HSV-1 as a Viral Infection Model.Viruses. 2025 Mar 14;17(3):416. doi: 10.3390/v17030416. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40143343 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying HSV-1 Inhibitors from Natural Compounds via Virtual Screening Targeting Surface Glycoprotein D.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Mar 16;15(3):361. doi: 10.3390/ph15030361. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35337158 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-HSV-1 agents: an update.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 21;15:1451083. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1451083. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39931518 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bollinger J M, Jr, Edmondson D E, Huynh B H, Filley J, Norton J R, Stubbe J. Mechanism of assembly of the tyrosyl radical-dinuclear iron cluster cofactor of ribonucleotide reductase. Science. 1991;253:292–298. - PubMed
-
- Brandt C R, Kintner R L, Pumfery A M, Visalli R J, Grau D R. The herpes simplex virus ribonucleotide reductase is required for ocular virulence. J Gen Virol. 1991;72:2043–2049. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

