Outer membrane profiles of clonally related Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from clinical samples and activities of cephalosporins and carbapenems
- PMID: 9660996
- PMCID: PMC105658
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.7.1636
Outer membrane profiles of clonally related Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from clinical samples and activities of cephalosporins and carbapenems
Abstract
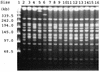
Fifteen isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs) isolated during a nosocomial outbreak were studied. The strains belonged to the same clonal type, as shown by pulsed-field gel electrophoretic analysis of chromosomal DNA. All the isolates were resistant to extended-spectrum cephalosporins, aztreonam, gentamicin, and fluoroquinolones and were susceptible to carbapenems, tobramycin, netilmicin, and amikacin. None of the isolates expressed the OmpK36 porin. Eight isolates, for which the MICs of cefoxitin were > or = 64 micrograms/ml, showed a diminished level or no expression of a 35-kDa porin. The MICs of meropenem, cefotaxime, and cefpirome were three to eight times higher for porin-deficient isolates than for isolates expressing the 35-kDa porin, but the MICs of imipenem increased two times for porin-deficient isolates compared to those for isolates expressing the porin. This MIC increase reverted to a level similar to that for the parental strain when porin-deficient isolates were transformed with the gene coding for the K. pneumoniae porin OmpK36. It is concluded that the high level of resistance to cefoxitin and the increase in the MICs of meropenem, cefotaxime, and cefpirome for the ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae isolates studied are associated with porin deficiency.
Figures



References
-
- Brun-Buisson C, Legrand P, Philippon A, Montravers F, Ansquer M, Dural J. Transferable enzymatic resistance to third-generation cephalosporins during nosocomial outbreak of multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Lancet. 1987;ii:302–306. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H. Y., and D. M. Livermore. 1993. Activity of cefepime and other β-lactam antibiotics against permeability mutants of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 32(Suppl. B):63–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

