Evaluation of moxifloxacin, a new 8-methoxyquinolone, for treatment of meningitis caused by a penicillin-resistant pneumococcus in rabbits
- PMID: 9661008
- PMCID: PMC105670
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.7.1706
Evaluation of moxifloxacin, a new 8-methoxyquinolone, for treatment of meningitis caused by a penicillin-resistant pneumococcus in rabbits
Abstract
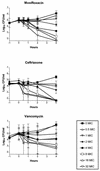
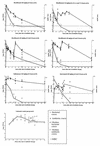
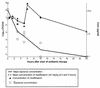
Moxifloxacin is a new 8-methoxyquinolone with high activity against gram-positive bacteria, including penicillin-resistant pneumococci. In an experimental meningitis model, we studied the pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in infected and uninfected rabbits and evaluated the antibiotic efficacies of moxifloxacin, ceftriaxone, and vancomycin against a penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae strain (penicillin, ceftriaxone, vancomycin, and moxifloxacin MICs were 1, 0.5, 0.5, and 0.125 microgram/ml, respectively). Moxifloxacin entered cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) readily, with peak values within 15 to 30 min after bolus intravenous infusion and with a mean percent penetration into normal and purulent CSF of approximately 50 and 80%, respectively. The bactericidal effect of moxifloxacin was concentration dependent, and regrowth was seen only when the concentration of moxifloxacin in CSF was below the minimal bactericidal concentration. All antibiotic-treated groups (moxifloxacin given in two doses of 40 mg/kg of body weight, moxifloxacin in two 20-mg/kg doses, ceftriaxone in one 125-mg/kg dose, and vancomycin in two 20-mg/kg doses) had significantly higher reductions in CSF bacterial concentration than the untreated group (P < 0.05). Moxifloxacin was as effective as vancomycin and ceftriaxone in reducing bacterial counts at all time points tested (3, 5, 10, and 24 h). Moreover, moxifloxacin given in two 40-mg/kg doses resulted in a significantly higher reduction in CSF bacterial concentration (in log10 CFU per milliliter) than vancomycin within 3 h after the start of antibiotic treatment (3.49 [2.94 to 4.78] versus 2.50 [0.30 to 3.05]; P < 0.05). These results indicate that moxifloxacin could be useful in the treatment of meningitis, including penicillin-resistant pneumococcal meningitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Garenoxacin (BMS-284756) and moxifloxacin in experimental meningitis caused by vancomycin-tolerant pneumococci.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Jan;47(1):211-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.1.211-215.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12499193 Free PMC article.
-
Moxifloxacin in the therapy of experimental pneumococcal meningitis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998 Jun;42(6):1397-407. doi: 10.1128/AAC.42.6.1397. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998. PMID: 9624483 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative in-vitro activity of moxifloxacin, penicillin, ceftriaxone and ciprofloxacin against pneumococci isolated from meningitis.J Antimicrob Chemother. 1999 Jun;43(6):833-5. doi: 10.1093/jac/43.6.833. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1999. PMID: 10404324
-
Penicillin-resistant streptococcus pneumoniae: review of moxifloxacin activity.Clin Infect Dis. 2001 Mar 15;32 Suppl 1:S22-9. doi: 10.1086/319372. Clin Infect Dis. 2001. PMID: 11249825 Review.
-
Treatment failure with use of a third-generation cephalosporin for penicillin-resistant pneumococcal meningitis: case report and review.Clin Infect Dis. 1994 Feb;18(2):188-93. doi: 10.1093/clinids/18.2.188. Clin Infect Dis. 1994. PMID: 8161625 Review.
Cited by
-
Design, synthesis, and protein methyltransferase activity of a unique set of constrained amine containing compounds.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Sep 15;26(18):4436-4440. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 27528434 Free PMC article.
-
Moxifloxacin: a review of its clinical potential in the management of community-acquired respiratory tract infections.Drugs. 2000 Jan;59(1):115-39. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200059010-00010. Drugs. 2000. PMID: 10718103 Review.
-
Garenoxacin (BMS-284756) and moxifloxacin in experimental meningitis caused by vancomycin-tolerant pneumococci.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Jan;47(1):211-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.1.211-215.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12499193 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of pneumococcal meningitis.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Jul;24(3):557-91. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00008-11. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21734248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential interactions of the extended-spectrum fluoroquinolones with the CNS.Drug Saf. 1999 Aug;21(2):123-35. doi: 10.2165/00002018-199921020-00005. Drug Saf. 1999. PMID: 10456380 Review.
References
-
- Bradley J S, Scheld W M. The challenge of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis: current antibiotic therapy in the 1990s. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;24:S213–S221. - PubMed
-
- Dalhoff A, Petersen U, Endermann R. In vitro activity of BAY 12-8039, a new 8-methoxyquinolone. Chemotherapy (Basel) 1996;42:410–425. - PubMed
-
- Decazes J M, Mohler J, Bure A, Vallois J M, Meulemans A, Modai J. Pharmacokinetics of fleroxacin and its metabolites in serum, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain of rabbits with and without experimental Escherichia coli meningitis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989;11:1208–1209.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

