Multiple neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas in von Hippel-Lindau disease patients: histopathological and molecular genetic analysis
- PMID: 9665483
- PMCID: PMC1852951
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65563-0
Multiple neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas in von Hippel-Lindau disease patients: histopathological and molecular genetic analysis
Abstract
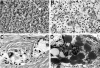
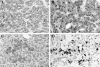
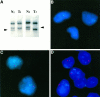
Although pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease have been reported, their pathological features have not been characterized. In addition, it is unknown whether alterations of the VHL gene are responsible for pancreatic NET development. To evaluate NETs in VHL patients, we performed histopathological analysis of 30 pancreatic tumors in 14 patients. In addition, DNA from NETs and normal pancreatic tissue from 6 patients with documented germ-line VHL gene mutations was studied for allelic deletions of the second copy of the VHL gene by fluorescence in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction-based single-strand conformational polymorphism analysis. Morphologically, the tumors were characterized by solid, trabecular, and/or glandular architecture and prominent stromal collagen bands. Sixty percent of the tumors revealed at least focally clear-cell cytology. All tumors were positive for panendocrine immunohistochemistry markers (chromogranin A and/or synaptophysin); 35% of NETs demonstrated focal positivity for pancreatic polypeptide, somatostatin, insulin, and/or glucagon; and no immunostaining for pancreatic and gastrointestinal hormones was observed in 65% of tumors. Dense core neurosecretory granules were evident by electron microscopic examination, and the clear cells additionally revealed abundant intracytoplasmic lipid. All NETs that were subjected to genetic analysis showed allelic loss of the second copy of the VHL gene. We conclude that multiple, nonfunctional pancreatic NETs occur in VHL patients. Stromal collagen bands and clear-cell morphology are important histological features of VHL-associated NETs. The presence of allelic deletions of the VHL gene in pancreatic NETs provides direct molecular evidence for a role of the gene in their tumorigenesis and establishes NET as an independent tumor type of VHL disease.
Figures
References
-
- Lamiell JM, Salazar FG, Hsia YE: Von Hippel-Lindau disease affecting 43 members of a single kindred. Medicine (Baltimore) 1989, 68:1-29 - PubMed
-
- Neumann HPH, Dinkel E, Brambs H, Wimmer B, Friedburg H, Volk B, Sigmund G, Riegler P, Haag K, Schollmeyer P, Wiestler OD: Pancreatic lesions in the von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Gastroenterology 1991, 101:465-471 - PubMed
-
- Hough MT, Stephens DH, Johnson CD, Binkovitz LA: Pancreatic lesions in von Hippel-Lindau disease: prevalence, clinical significance, and CT findings. Am J Roentgenol 1994, 162:1091-1094 - PubMed
-
- Binkovitz LA, Johnson CD, Stephens DH: Islet cell tumors in von Hippel-Lindau disease: increased prevalence and relationship to the multiple endocrine neoplasias. Am J Roentgenol 1990, 155:501-505 - PubMed
-
- Latif F, Tory K, Gnarra J, Yao M, Duh F-M, Orcutt M, Stackhouse T, Kuzmin I, Modi W, Geil L, Schmidt L, Zhou F, Li H, Wei M, Chen F, Glenn G, Choyke P, Walther M, Weng Y, Duan D, Dean M, glavac D, Richards F, Crossey P, Ferguson-Smith M, Paslier D, Chumakov I, Cohen D, Chinault A, Maher E, Linehan W, Zbar B, Lerman M: Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science 1993, 260:1317-1320 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

