Concentrations of circulating beta-chemokines do not correlate with viral load in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals
- PMID: 9665956
- PMCID: PMC95607
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.5.4.499-502.1998
Concentrations of circulating beta-chemokines do not correlate with viral load in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals
Abstract
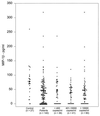
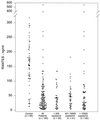
The CC or beta-chemokines MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, and RANTES are the primary components of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-suppressive soluble factors in vitro. We studied the relationship between the concentrations of MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, and RANTES in plasma and HIV viral load in HIV-infected subjects. The HIV-positive patient group (n = 140) had significantly lower concentrations of all three beta-chemokines (MIP-1alpha, P < 0.0005; MIP-1beta, P < 0.005; RANTES, P < 0.0005) than the control group (n = 58 for MIP-1alpha, n = 27 for MIP-1beta, and n = 59 for RANTES). In addition, we divided the patient group into three subgroups (high, moderate, and low) based on the number of HIV-1 RNA copies in the plasma (as measured by quantitative HIV RNA PCR). Again, all three subgroups had significantly lower concentrations of the beta-chemokines than the HIV-negative control group. However, there was no significant difference in plasma beta-chemokine concentrations among the three subgroups within the patient group (P < 0.3). Although our results demonstrate that HIV-infected individuals had significantly lower concentrations of circulating beta-chemokines than healthy uninfected control subjects, we found no correlation between the concentrations of beta-chemokines in plasma and HIV-1 viral load in HIV-infected individuals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circulating levels and ex vivo production of beta-chemokines, interferon gamma, and interleukin 2 in advanced human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection: the effect of protease inhibitor therapy.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Jun 10;16(9):835-43. doi: 10.1089/08892220050042774. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 10875609 Clinical Trial.
-
Positive association between beta-chemokine-producing T cells and HIV type 1 viral load in HIV-infected subjects in Abidjan, Côte d'Ivoire.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2002 Feb 10;18(3):171-7. doi: 10.1089/08892220252781220. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2002. PMID: 11839151
-
Endogenous production of beta-chemokines by CD4+, but not CD8+, T-cell clones correlates with the clinical state of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected individuals and may be responsible for blocking infection with non-syncytium-inducing HIV-1 in vitro.J Virol. 1998 Jan;72(1):876-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.1.876-881.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9420304 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of good correlation of serum CC-chemokine levels with human immunodeficiency virus-1 disease stage and response to treatment.J Lab Clin Med. 2004 May;143(5):310-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lab.2004.01.012. J Lab Clin Med. 2004. PMID: 15122175
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of MIP-1α and MIP-1β Chemokines in Malaria in Relation to Disease Severity.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Apr 6;61(4):676. doi: 10.3390/medicina61040676. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40282967 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Reduced CCR5 Expression and Immune Quiescence in Black South African HIV-1 Controllers.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 20;12:781263. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.781263. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34987508 Free PMC article.
-
Higher macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha and MIP-1beta levels from CD8+ T cells are associated with asymptomatic HIV-1 infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 5;97(25):13812-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.240469997. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11095721 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Sample Selection Approach to Aid the Identification of Factors That Correlate With the Control of HIV-1 Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 11;12:634832. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.634832. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33777023 Free PMC article.
-
Increased levels of circulating cytokines with HIV-related immunosuppression.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2012 Aug;28(8):809-15. doi: 10.1089/AID.2011.0144. Epub 2011 Dec 2. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2012. PMID: 21962239 Free PMC article.
-
The CC-chemokine RANTES increases the attachment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to target cells via glycosaminoglycans and also activates a signal transduction pathway that enhances viral infectivity.J Virol. 1999 Aug;73(8):6370-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.6370-6379.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10400729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1α, MIP-1β receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Atchison R E, Gosling J, Monteclaro F S, Franci C, Digilio L, Charo I F, Goldsmith M A. Multiple extracellular elements of CCR5 and HIV-1 entry: dissociation from response to chemokines. Science. 1996;274:1924–1926. - PubMed
-
- Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B. Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines—CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:97–179. - PubMed
-
- Bleul C C, Farzan M, Choe H, Parolin C, Clark-Lewis I, Sodroski J, Springer T A. The lymphocyte chemoattractant SDF-1 is a ligand for LESTR/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature. 1996;382:829–832. - PubMed
-
- Cocchi F, DeVico A L, Garzino-Demo A, Arya S K, Gallo R C, Lusso P. Identification of RANTES, MIP-1α, and MIP-1β as the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T cells. Science. 1995;270:1811–1815. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

