Immune pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 9670046
- PMCID: PMC2212453
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.2.341
Immune pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
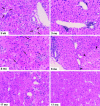
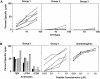
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common complication of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The pathogenetic mechanisms potentially responsible for HCC during chronic HBV infection are not well defined. This study demonstrates that chronic immune-mediated liver cell injury triggers the development of HCC in the absence of viral transactivation, insertional mutagenesis, and genotoxic chemicals. These results strongly suggest that the immune response to HBV is both necessary and sufficient to cause liver cancer during chronic HBV infection, and that all other procarcinogenic events associated with HCC are probably dependent on this process.
Figures


References
-
- Chisari FV, Ferrari C. Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:29–60. - PubMed
-
- Tsai SL, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Yang PM, Sung JL, Huang JH, Hwang LH, Chang TH, Chen DS. Acute exacerbations of chronic type B hepatitis are accompanied by increased T cell responses to hepatitis B core and e antigens. Implications for hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion. J Clin Invest. 1992;89:87–96. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Colombo M, de Franchis R, Del Ninno E, Sangiovanni A, De Fazio C, Tommasini M, Donato MF, Piva A, Di Carlo V, Dioguardi N. Hepatocellular carcinoma in Italian patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:675–680. - PubMed
-
- Okuda K. Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent progress. Hepatology. 1992;15:948–963. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda K, Saitoh S, Koida I, Arase Y, Tsubota A, Chayama K, Kumada H, Kawanishi M. A multivariate analysis of risk factors for hepatocellular carcinogenesis: a prospective observation of 795 patients with viral and alcoholic cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1993;18:47–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

