Transcription factor Pip can enhance DNA binding by E47, leading to transcriptional synergy involving multiple protein domains
- PMID: 9671474
- PMCID: PMC109050
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.8.4639
Transcription factor Pip can enhance DNA binding by E47, leading to transcriptional synergy involving multiple protein domains
Abstract
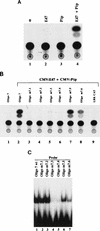
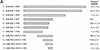
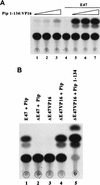
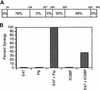
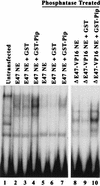
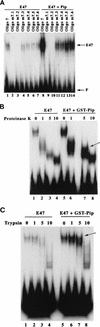
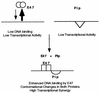
The transcription factors E2A (E12/E47) and Pip are both required for normal B-cell development. Each protein binds to regulatory sequences within various immunoglobulin enhancer elements. Activity of E2A proteins can be regulated by interactions with other proteins which influence their DNA binding or activation potential. Similarly, Pip function can be influenced by interaction with the protein PU.1, which can recruit Pip to bind to DNA. We show here that a previously unidentified Pip binding site resides adjacent to the E2A binding site within the immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer. Both of these binding sites are crucial for high-level enhancer activity. We found that E47 and Pip can functionally interact to generate a very potent 100-fold transcriptional synergy. Through a series of mutagenesis experiments, we identified the Pip sequences necessary for transcriptional activation and for synergy with E47. Two synergy domains (residues 140 to 207 and 300 to 420) in addition to the Pip DNA binding domain (residues 1 to 134) are required for maximal synergy with E47. We also identified a Pip domain (residues 207 to 300) that appears to mask Pip transactivation potential. Part of the synergy mechanism between E47 and Pip appears to involve the ability of Pip to increase DNA binding by E47, perhaps by inducing a conformational change in the E47 protein. E47 may also induce a conformational change in Pip which unmasks sequences important for transcriptional activity. Based upon our results, we propose a model for E47-Pip transcriptional synergy.
Figures




References
-
- Atchison M L, Perry R P. The role of the κ enhancer and its binding factor NF-κB in the developmental regulation of κ gene transcription. Cell. 1987;48:121–127. - PubMed
-
- Bain G, Maandag E C R, Izon D J, Amsen D, Kruisbeek A M, Weintraub B C, Krop I, Schlissel M S, Feeney A J, van Roon M, van der Valk M, te Riele H P J, Berns A, Murre C. E2A proteins are required for proper B cell development and initiation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Cell. 1994;79:885–892. - PubMed
-
- Benezra R. An intermolecular disulfide bond stabilizes E2A homodimers and is required for DNA binding at physiological temperatures. Cell. 1994;79:1057–1067. - PubMed
-
- Benezra R, Davis R L, Lockshon D, Turner D L, Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990;61:49–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
