Male-specific transcription initiation of the C4-Slp gene in mouse liver follows activation of STAT5
- PMID: 9671750
- PMCID: PMC21148
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.15.8750
Male-specific transcription initiation of the C4-Slp gene in mouse liver follows activation of STAT5
Abstract
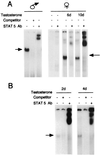
The mouse genes encoding the constitutively expressed complement component C4 and its closely related isoform C4-Slp (sex-limited protein), which is expressed only in male animals of several strains, provide a unique model to study sequence elements and trans-acting factors responsible for androgen responsiveness. Our previous studies have shown that hormonal induction of C4-Slp is mediated by a sex-specific pattern of growth hormone secretion. Promoter analyses in vitro have led to contradictory conclusions concerning the significance of C4-Slp-specific sequences in the 5' flanking region. Mutant mice carrying the H-2(aw18) haplotype, which is characterized by a large deletion in the S region covering the C4 and 21-OHase A genes, permit the direct in vivo analysis of C4-Slp transcription, unhindered by the presence of C4. Run-on analysis of transcription in liver nuclei of males and females of this strain demonstrated a 100-fold higher transcriptional activity in males, essentially determined at the transcription initiation level. The androgen dependence of transcription initiation was confirmed by run-on analysis of testosterone-treated females, where transcriptional activity started after 6 days of androgen treatment and reached male levels after 20 days. Conversely, the growth hormone-regulated activity of transcription factor STAT5 was already detected in liver nuclei after 48 hr of androgen treatment. Furthermore, we demonstrate that activated STAT5 recognizes in vitro two upstream gamma interferon-activated sequence (GAS) elements of the C4-Slp gene, centered at positions -1969 and -1831. We postulate that binding of STAT5 to these C4-Slp-specific GAS elements plays a crucial role in the chromatin remodelings that lead to transcriptional competence of the C4-Slp gene in the liver.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Male-specific expression of mouse sex-limited protein requires growth hormone, not testosterone.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3626-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3626. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8475111 Free PMC article.
-
The androgen-dependent C4-Slp gene is driven by a constitutively competent promoter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5786-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5786. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8390682 Free PMC article.
-
Two distinct mechanisms elicit androgen-dependent expression of the mouse sex-limited protein gene.Mol Endocrinol. 1997 Apr;11(4):460-9. doi: 10.1210/mend.11.4.9912. Mol Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9092798
-
Structure and expression of murine fourth complement component (C4) and sex-limited protein (Slp).Immunol Rev. 1985 Oct;87:101-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01147.x. Immunol Rev. 1985. PMID: 3902619 Review.
-
The C4 and Slp genes of the complement region of the murine H-2 major histocompatibility complex.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 6;306(1129):395-403. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0100. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984. PMID: 6149582 Review.
Cited by
-
Transgenic mice showing inflammation-inducible overexpression of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004 May;11(3):588-98. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.11.3.588-598.2004. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15138187 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of sex-limitation KRAB zinc finger proteins modulate sex-dependent and -independent liver metabolism.Physiol Genomics. 2009 Jun 10;38(1):16-28. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.90391.2008. Epub 2009 Apr 7. Physiol Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19351907 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

