Passive immunization with antibodies against three distinct epitopes on Plasmodium yoelii merozoite surface protein 1 suppresses parasitemia
- PMID: 9673281
- PMCID: PMC108453
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.8.3925-3930.1998
Passive immunization with antibodies against three distinct epitopes on Plasmodium yoelii merozoite surface protein 1 suppresses parasitemia
Abstract
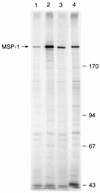
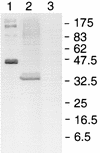
We have produced monoclonal antibodies against Plasmodium yoelii merozoite surface protein 1 (MSP-1) and have assessed their ability to suppress blood stage parasitemia by passive immunization. Six immunoglobulin G antibodies were characterized in detail: three (B6, D3, and F5) were effective in suppressing a lethal blood stage challenge infection, two (B10 and G3) were partially effective, and one (B4) was ineffective. MSP-1 is the precursor to a complex of polypeptides on the merozoite surface; all of the antibodies bound to this precursor and to an approximately 42-kDa fragment (MSP-142) that is derived from the C terminus of MSP-1. MSP-142 is further cleaved to an N-terminal approximately 33-kDa polypeptide (MSP-133) and a C-terminal approximately 19-kDa polypeptide (MSP-119) comprised of two epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like modules. D3 reacted with MSP-142 but not with either of the constituents MSP-133 and MSP-119, B4 recognized an epitope within the N terminus of MSP-133, and B6, B10, F5, and G3 bound to MSP-119. B10 and G3 bound to epitopes that required both C-terminal EGF-like modules for their formation, whereas B6 and F5 bound to epitopes in the first EGF-like module. These results indicate that at least three distinct epitopes on P. yoelii MSP-1 are recognized by antibodies that suppress parasitemia in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Akerstrom B, Brodin T, Reis K, Bjorck L. Protein G: a powerful tool for binding and detection of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1985;135:2589–2592. - PubMed
-
- Blackman M J, Ling I T, Nicholls S C, Holder A A. Proteolytic processing of the Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface protein-1 produces a membrane-bound fragment containing two epidermal growth factor-like domains. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991;49:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Blackman M J, Dennis E D, Hirst E M A, Kocken C H, Scott-Finnigan T J, Thomas A W. Plasmodium knowlesi: secondary processing of the malaria merozoite surface protein-1. Exp Parasitol. 1996;83:229–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

