Determinants of specificity in TGF-beta signal transduction
- PMID: 9679059
- PMCID: PMC317013
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.14.2144
Determinants of specificity in TGF-beta signal transduction
Abstract
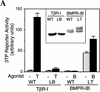
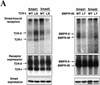
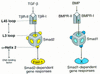
Signal transduction by the TGF-beta family involves sets of receptor serine/threonine kinases, Smad proteins that act as receptor substrates, and Smad-associated transcription factors that target specific genes. We have identified discrete structural elements that dictate the selective interactions between receptors and Smads and between Smads and transcription factors in the TGF-beta and BMP pathways. A cluster of four residues in the L45 loop of the type I receptor kinase domain, and a matching set of two residues in the L3 loop of the Smad carboxy-terminal domain establish the specificity of receptor-Smad interactions. A cluster of residues in the highly exposed alpha-helix 2 of the Smad carboxy-terminal domain specify the interaction with the DNA-binding factor Fast1 and, as a result, the gene responses mediated by the pathway. By establishing specific interactions, these determinants keep the TGF-beta and BMP pathways segregated from each other.
Figures
















References
-
- Baker J, Harland RM. A novel mesoderm inducer, mMadr-2, functions in the activin signal transduction pathway. Genes & Dev. 1996;10:1880–1889. - PubMed
-
- Candia AF, Watabe T, Hawley SH, Onichtchouck D, Zhang Y, Derynck R, Niehrs C, Cho KW. Cellular interpretation of multiple TGF-β signals: Intracellular antagonism between activin/BVg1 and BMP-2/4 signaling mediated by Smads. Development. 1997;124:4467–4480. - PubMed
-
- Cheifetz S, Hernandez H, Laiho M, ten Dijke P, Iwata KK, Massagué J. Distinct transforming growth factor-β receptor subsets as determinants of cellular responsiveness to three TGF-β isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:20533–20538. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
