EIR1, a root-specific protein involved in auxin transport, is required for gravitropism in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 9679062
- PMCID: PMC317016
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.14.2175
EIR1, a root-specific protein involved in auxin transport, is required for gravitropism in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
The EIR1 gene of Arabidopsis is a member of a family of plant genes with similarities to bacterial membrane transporters. This gene is expressed only in the root, which is consistent with the phenotypes of the eir1 mutants-the roots are agravitropic and have a reduced sensitivity to ethylene. The roots of eir1 mutants are also insensitive to the excess auxin produced by alf1-1 and fail to induce an auxin-inducible gene in the expansion zone. Although they fail to respond to internally generated auxin, they respond normally to externally applied auxin. Expression of the EIR1 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae confers resistance to fluorinated indolic compounds. Taken together, these data suggest that the EIR1 protein has a root-specific role in the transport of auxin.
Figures


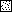 ) eir1-3]. Root elongation determined
at 12 DAG was normalized to root growth on unsupplemented medium
(100%). Standard deviations are shown as bars; molarities used are
indicated.
) eir1-3]. Root elongation determined
at 12 DAG was normalized to root growth on unsupplemented medium
(100%). Standard deviations are shown as bars; molarities used are
indicated.

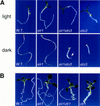
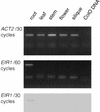

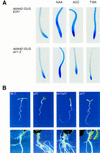
References
-
- Abel S, Ballas N, Wong L-M, Theologis A. DNA elements responsive to auxin. BioEssays. 1996;18:647–654. - PubMed
-
- Abel S, Nguyen MD, Theologis A. The PS-IAA4/5-like family of early auxin-inducible mRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Mol Biol. 1995;251:533–549. - PubMed
-
- Adams MD, Wagner LM, Graddis TJ, Landick R, Antonucci TK, Gibson AL, Oxender DL. Nucleotide sequence and genetic characterization reveal six essential genes for the LIV-I and LS transport systems of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:11436–11443. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, NY: John Wiley/Greene; 1987.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
