Translation of the chloroplast psbA mRNA requires the nuclear-encoded poly(A)-binding protein, RB47
- PMID: 9679142
- PMCID: PMC2133045
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.2.435
Translation of the chloroplast psbA mRNA requires the nuclear-encoded poly(A)-binding protein, RB47
Abstract
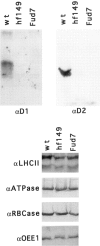
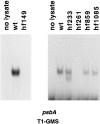
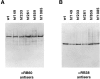
A set of nuclear mutants of C. reinhardtii were identified that specifically lack translation of the chloroplast-encoded psbA mRNA, which encodes the photosystem II reaction center polypeptide D1. Two of these mutants are deficient in the 47-kD member (RB47) of the psbA RNA-binding complex, which has previously been identified both genetically and biochemically as a putative translational activator of the chloroplast psbA mRNA. RB47 is a member of the poly(A)-binding protein family, and binds with high affinity and specificity to the 5' untranslated region of the psbA mRNA. The results presented here confirm RB47's role as a message-specific translational activator in the chloroplast, and bring together genetic and biochemical data to form a cohesive model for light- activated translational regulation in the chloroplast.
Figures



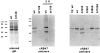

References
-
- Bag J, Wu J. Translational control of poly(A)-binding protein expression. Eur J Biochem. 1996;237:143–152. - PubMed
-
- Bennoun, P., and P. Delepelaire. 1982. Isolation of photosynthesis mutants in Chlamydomonas. In Methods in Chloroplast Molecular Biology. M. Edelman, R.B. Hallick, and N.-H. Chua, editors. Elsevier Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 25–38.
-
- Bennoun P, Spierer-Herz M, Erickson J, Girard-Bascou J, Pierre Y, Delsome M, Rochaix J-D. Characterization of photosystem II mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii lacking the psbAgene. Plant Mol Biol. 1986;6:151–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

