A-kinase anchoring protein 100 (AKAP100) is localized in multiple subcellular compartments in the adult rat heart
- PMID: 9679148
- PMCID: PMC2133049
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.2.511
A-kinase anchoring protein 100 (AKAP100) is localized in multiple subcellular compartments in the adult rat heart
Abstract
Stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors activates type I and II cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A, resulting in phosphorylation of various proteins in the heart. It has been proposed that PKA II compartmentalization by A-kinase-anchoring proteins (AKAPs) regulates cyclic AMP-dependent signaling in the cell. We investigated the expression and localization of AKAP100 in adult hearts. By immunoblotting, we identified AKAP100 in adult rat and human hearts, and showed that type I and II regulatory (RI and II) subunits of PKA are present in the rat heart. By immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy of rat cardiac myocytes and cryostat sections of rat left ventricle papillary muscles, we localized AKAP100 to the nucleus, sarcolemma, intercalated disc, and at the level of the Z-line. After double immunostaining of transverse cross-sections of the papillary muscles with AKAP100 plus alpha-actinin-specific antibodies or AKAP100 plus ryanodine receptor-specific antibodies, confocal images showed AKAP100 localization at the region of the transverse tubule/junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum. RI is distributed differently from RII in the myocytes. RII, but not RI, was colocalized with AKAP100 in the rat heart. Our studies suggest that AKAP100 tethers PKA II to multiple subcellular compartments for phosphorylation of different pools of substrate proteins in the heart.
Figures
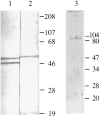

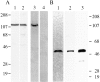

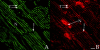













Similar articles
-
Cloning and characterization of A-kinase anchor protein 100 (AKAP100). A protein that targets A-kinase to the sarcoplasmic reticulum.J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 21;270(16):9327-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.16.9327. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7721854
-
AKAP-mediated targeting of protein kinase a regulates contractility in cardiac myocytes.Circ Res. 2001 Feb 16;88(3):291-7. doi: 10.1161/01.res.88.3.291. Circ Res. 2001. PMID: 11179196
-
Selectivity and regulation of A-kinase anchoring proteins in the heart. The role of autophosphorylation of the type II regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase.J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 29;275(52):41389-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004212200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10993882
-
Anchoring and scaffold proteins for kinases and phosphatases.Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997;52:409-29; discussion 429-30. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997. PMID: 9238861 Review.
-
AKAP mediated signal transduction.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002;42:235-57. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.42.083101.135801. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 11807172 Review.
Cited by
-
AKAP-scaffolding proteins and regulation of cardiac physiology.Physiology (Bethesda). 2009 Apr;24:78-87. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00041.2008. Physiology (Bethesda). 2009. PMID: 19364910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compartmentalization role of A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) in mediating protein kinase A (PKA) signaling and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Dec 24;16(1):218-29. doi: 10.3390/ijms16010218. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25547489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mAKAP assembles a protein kinase A/PDE4 phosphodiesterase cAMP signaling module.EMBO J. 2001 Apr 17;20(8):1921-30. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.8.1921. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11296225 Free PMC article.
-
Networking with AKAPs: context-dependent regulation of anchored enzymes.Mol Interv. 2010 Apr;10(2):86-97. doi: 10.1124/mi.10.2.6. Mol Interv. 2010. PMID: 20368369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mAKAP-a master scaffold for cardiac remodeling.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;65(3):218-25. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000206. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25551320 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beall JA, Mitchell GF. Identification of a particular antigen from a parasite cDNA library using antibodies affinity purified from selected portions of Western blot. J Immunol Methods. 1986;86:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Bregman DB, Bhattacharyya N, Rubin CS. High affinity binding protein for the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II-B. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:4648–4656. - PubMed
-
- Burton KA, Johnson BD, Hausken ZE, Westenbroek RE, Idzerda RL, Scheuer T, Scott JD, Catterall WA, McKnight GS. Type II regulatory subunits are not required for the anchoring-dependent modulation of Ca21 channel activity by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:11067–11072. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carr DW, Hausken ZE, Fraser IDC, Stofko-Hahn RE, Scott JD. Association of the type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase with a human thyroid RII-anchoring protein. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13376–13382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

