Vasopressin, angiotensin II and renal responses during water immersion in hydrated humans
- PMID: 9679185
- PMCID: PMC2231110
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.323bi.x
Vasopressin, angiotensin II and renal responses during water immersion in hydrated humans
Abstract
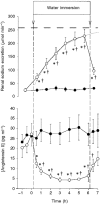
1. The hypothesis was tested that in hydrated humans the release of arginine vasopressin and angiotensin II is suppressed by water immersion (WI) and that this is a mechanism of the immersion-induced diuresis and natriuresis. Seven male subjects on controlled sodium (65-75 mmol per 24 h for 4 days) and water intake were studied. 2. Plasma vasopressin was promptly suppressed by WI, declining from 0. 76 +/- 0.13 to 0.23 +/- 0.08 pg ml-1 (P < 0.05), with a concomitant increase in renal water output (CH2O) from -0.4 +/- 0.2 to 4.4 +/- 0.7 ml min-1 (P < 0.05). Subsequently, CH2O returned to the level of control, whereas plasma vasopressin remained suppressed. Plasma osmolality gradually increased from 285 +/- 1 to 289 +/- 1 mosmol kg-1 (P < 0.05). WI caused a 9-fold increase in renal sodium excretion. Plasma angiotensin II decreased from 27.1 +/- 5.3 to 4.3 +/- 0.7 pg ml-1 (P < 0.05), and the intraindividual correlation coefficients between sodium excretion rates and angiotensin II concentrations varied between 0.73 and 0.96 (P < 0.002). 3. The data demonstrate that plasma vasopressin and angiotensin II concentrations decrease during WI in hydrated humans, concomitantly with initial increases in CH2O and sodium excretion. Therefore, vasopressin could constitute a mediator of CH2O and angiotensin II of the natriuresis of WI. The subsequent return of CH2O to the level of control is, however, also caused by other factors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroendocrine and renal effects of intravascular volume expansion in compensated heart failure.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001 Aug;281(2):R459-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.2001.281.2.R459. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11448848 Clinical Trial.
-
Hormonal regulation of renal sodium and water excretion during normotensive sodium loading in conscious dogs.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000 Jan;278(1):R11-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.2000.278.1.R11. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10644616
-
Arginine vasopressin, circulation, and kidney during graded water immersion in humans.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1986 Aug;61(2):565-74. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.2.565. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1986. PMID: 3745047
-
The defence of plasma osmolality.J Physiol (Paris). 1984;79(6):416-20. J Physiol (Paris). 1984. PMID: 6399309 Review.
-
Mechanisms of sodium balance in hypertension: role of pressure natriuresis.J Hypertens Suppl. 1986 Oct;4(4):S57-65. J Hypertens Suppl. 1986. PMID: 3021942 Review.
Cited by
-
Whole body immersion and hydromineral homeostasis: effect of water temperature.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010 Jan;108(1):49-58. doi: 10.1007/s00421-009-1187-2. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19756708
-
The effects of hydrotherapy on anxiety, pain, neuroendocrine responses, and contraction dynamics during labor.Biol Res Nurs. 2010 Jul;12(1):28-36. doi: 10.1177/1099800410361535. Epub 2010 May 7. Biol Res Nurs. 2010. PMID: 20453024 Free PMC article.
-
Reviewing the current methods of assessing hydration in athletes.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020 Oct 30;17(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12970-020-00381-6. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33126891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adrenomedullin and elements of orthostatic competence after 41 h of voluntary submersion in water as measured in four healthy males.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006 Apr;96(6):644-50. doi: 10.1007/s00421-005-0122-4. Epub 2006 Jan 14. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16416151
-
Short-Term Effects of Land-Based Versus Water-Based Resistance Training Protocols on Post-Exercise Hypotension in Normotensive Men: A Crossover Study.Sports (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;10(11):181. doi: 10.3390/sports10110181. Sports (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson JV, Donckier J, Payne NN, Beacham J, Slater JDH, Bloom S R. Atrial natriuretic peptide: Evidence of action as a natriuretic hormone at physiological plasma concentrations in man. Clinical Science. 1987;72:305–312. - PubMed
-
- Casals-Stenzel J, Schmalbach J, Losert W. Acute effects of aldosterone antagonists in volunteers. In: Addison GM, Asmussen NW, Corvol P, Kloppenborg PWC, Norman N, Schröder R, Robertson JIS, editors. Aldosterone Antagonists in Clinical Medicine. Amsterdam and Oxford: Excerpta Medica; 1978. pp. 207–216.
-
- Emmeluth C, Drummer C, Gerzer R, Bie P. Natriuresis in conscious dogs caused by increased carotid Na+ during angiotensin II and aldosterone blockade. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. 1994;151:403–411. - PubMed
-
- Epstein M. Renal effects of head-out water immersion in humans: a 15-year update. Physiological Reviews. 1992;72:563–621. - PubMed
-
- Epstein M, Denunzio AG, Loutzenhiser RD. Effects of vasopressin administration on diuresis of water immersion in normal humans. Journal of Applied Physiology. 1981;51:1384–1387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

