Resource allocation and resident outcomes in nursing homes: comparisons between the best and worst
- PMID: 9679807
- PMCID: PMC1993888
- DOI: 10.1002/(sici)1098-240x(199808)21:4<297::aid-nur3>3.0.co;2-a
Resource allocation and resident outcomes in nursing homes: comparisons between the best and worst
Abstract
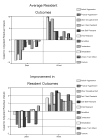
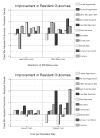
The purpose of this study was to identify patterns of resource allocation that relate to resident outcomes in nursing homes. Data on structure, staffing levels, salaries, cost, case mix, and resident outcomes were obtained from state-level, administrative databases on 494 nursing homes. We identified two sets of comparison groups and showed that the group of homes with the greatest percentage of improvement in resident outcomes had higher levels of registered nurse (RN) staffing and higher costs. However, comparison groups based on best-worst average outcomes did not differ in resource allocation patterns. Additional analysis demonstrated that when controlling for RN staffing, resident outcomes in high- and low-cost homes did not differ. The results suggest that, although RN staffing is more expensive, it is key to improving resident outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- Aaronson WE, Zinn JS, Rosko MD. Do for-profit and not-for-profit nursing homes behave differently? Gerontologist. 1994;34:775–786. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, R. A., Issel, L. M., & McDaniel, R. R. (in press). Nursing staff turnover in nursing homes: A new look. Public Administration Quarterly.
-
- Berlowitz DR, Ash AS, Brandeis GH, Brand HK, Halpern JL, Moskowitz MA. Rating long-term care facilities on pressure ulcer development: Importance of case-mix adjustment. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1996;124:557–563. - PubMed
-
- Bettis RA. Strategic management and the straightjacket: An editorial essay. Organization Science. 1991;2:315–319.
-
- Braun BI. The effect of nursing home quality on patient outcome. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 1991;39:329–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
