Photosynthetic electron transport involved in PxcA-dependent proton extrusion in Synechocystis sp. Strain PCC6803: effect of pxcA inactivation on CO2, HCO3-, and NO3- uptake
- PMID: 9683474
- PMCID: PMC107361
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.15.3799-3803.1998
Photosynthetic electron transport involved in PxcA-dependent proton extrusion in Synechocystis sp. Strain PCC6803: effect of pxcA inactivation on CO2, HCO3-, and NO3- uptake
Abstract
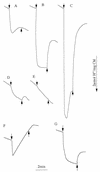
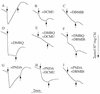
The product of pxcA (formerly known as cotA) is involved in light-induced Na+-dependent proton extrusion. In the presence of 2, 5-dimethyl-p-benzoquinone, net proton extrusion by Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803 ceased after 1 min of illumination and a postillumination influx of protons was observed, suggesting that the PxcA-dependent, light-dependent proton extrusion equilibrates with a light-independent influx of protons. A photosystem I (PS I) deletion mutant extruded a large number of protons in the light. Thus, PS II-dependent electron transfer and proton translocation are major factors in light-driven proton extrusion, presumably mediated by ATP synthesis. Inhibition of CO2 fixation by glyceraldehyde in a cytochrome c oxidase (COX) deletion mutant strongly inhibited the proton extrusion. Leakage of PS II-generated electrons to oxygen via COX appears to be required for proton extrusion when CO2 fixation is inhibited. At pH 8.0, NO3- uptake activity was very low in the pxcA mutant at low [Na+] (approximately 100 microM). At pH 6.5, the pxcA strain did not take up CO2 or NO3- at low [Na+] and showed very low CO2 uptake activity even at 15 mM Na+. A possible role of PxcA-dependent proton exchange in charge and pH homeostasis during uptake of CO2, HCO3-, and NO3- is discussed.
Figures



References
-
- Elstner E F, Zeller H. Bleaching of p-nitrosodimethylaniline by photosystem 1 of spinach lamellae. Plant Sci Lett. 1978;13:15–20.
-
- Hawkesford M J, Rowell P, Stewart W D P. Energy transduction in cyanobacteria. In: Papageorgiou G C, Packer L, editors. Photosynthetic prokaryotes: cell differentiation and function. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier; 1963. pp. 199–218.
-
- Hinrichs I, Scherer S, Boger P. Two different mechanisms of light induced proton efflux in the blue-green alga Anabaena variabilis. Physiol Veg. 1985;23:717–724.
-
- Kaneko T, Sato S, Kotani H, Tanaka A, Asamizu E, Nakamura Y, Miyajima N, Hirosawa M, Sugiura M, Sasamoto S, Kimura T, Hosouchi T, Matsuno A, Muraki A, Nakazaki N, Naruo K, Okumura S, Shimpo S, Takeuchi C, Wada T, Watanabe A, Yamada M, Yasuda M, Tabata S. Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. II. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions. DNA Res. 1996;3:109–136. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan A, Schwarz R, Lieman-Hurwitz J, Ronen-Tarazi M, Reinhold L. Physiological and molecular studies on the response of cyanobacteria to changes in the ambient inorganic carbon concentration. In: Bryant D A, editor. The molecular biology of cyanobacteria. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1994. pp. 469–485.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

