Disruption of the Candida albicans TPS1 gene encoding trehalose-6-phosphate synthase impairs formation of hyphae and decreases infectivity
- PMID: 9683476
- PMCID: PMC107363
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.15.3809-3815.1998
Disruption of the Candida albicans TPS1 gene encoding trehalose-6-phosphate synthase impairs formation of hyphae and decreases infectivity
Abstract
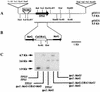
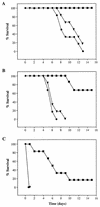
The TPS1 gene from Candida albicans, which encodes trehalose-6-phosphate synthase, has been cloned by functional complementation of a tps1 mutant from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In contrast with the wild-type strain, the double tps1/tps1 disruptant did not accumulate trehalose at stationary phase or after heat shock. Growth of the tps1/tps1 disruptant at 30 degreesC was indistinguishable from that of the wild type. However, at 42 degreesC it did not grow on glucose or fructose but grew normally on galactose or glycerol. At 37 degreesC, the yeast-hypha transition in the mutant in glucose-calf serum medium did not occur. During growth at 42 degreesC, the mutant did not form hyphae in galactose or in glycerol. Some of the growth defects observed may be traced to an unbalanced sugar metabolism that reduces the cellular content of ATP. Mice inoculated with 10(6) CFU of the tps1/tps1 mutant did not show visible symptoms of infection 16 days after inoculation, while those similarly inoculated with wild-type cells were dead 12 days after inoculation.
Figures


References
-
- Bell W, Klaasen P, Ohnacker M, Boller T, Herweijer M, Schoppink P, van der Zee P, Wiemken A. Characterization of the 56 kDA subunit of yeast trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and cloning of its gene reveal its identity with the product of CIF1, a regulator of carbon catabolite inactivation. Eur J Biochem. 1992;209:951–959. - PubMed
-
- Bergmeyer H U. Methods of enzymatic analysis. Weinheim, Germany: Verlag Chemie; 1983.
-
- Blázquez M A. Un nuevo mecanismo de control de la glicolisis en Saccharomyces cerevisiae: la inhibición de las hexokinasas por trehalosa-6-fosfato. PhD. thesis. Madrid, Spain: Faculty of Sciences, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid; 1995.
-
- Blázquez M A, Gancedo C. Identification of extragenic suppressors of the cif1 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1994;25:89–94. - PubMed
-
- Blázquez M A, Gancedo C. Mode of action of the qcr9 and cat3 mutations in restoring the ability of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tps1 mutants to grow on glucose. Mol Gen Genet. 1995;249:665–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

