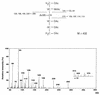
Chemical structure of lipid A isolated from Flavobacterium meningosepticum lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 9683486
- PMCID: PMC107373
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.15.3891-3899.1998
Chemical structure of lipid A isolated from Flavobacterium meningosepticum lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
The chemical structure of the lipid A of the lipopolysaccharide component isolated from Flavobacterium meningosepticum IFO 12535 was elucidated. Methylation and nuclear magnetic resonance analyses showed that two kinds of hydrophilic backbone exist in the free lipid A: a beta (1-->6)-linked 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose, which is usually present in enterobacterial lipid A's, and a 2-amino-6-O-(2, 3-diamino-2,3-dideoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-2-deoxy-D-glucose, in a molar ratio of 1.00:0.35. Both backbones were alpha-glycosidically phosphorylated in position 1, and the hydroxyl groups at positions 4, 4', and 6' were unsubstituted. Liquid secondary ion-mass spectrometry revealed a pseudomolecular ion at m/z 1673 [M-H]- as a major monophosphoryl lipid A component carrying five acyl groups. Fatty acid analysis showed that the lipid A contained 1 mol each of amide-linked (R)-3-OH iC17:0, ester-linked (R)-3-OH iC15:0, amide-linked (R)-3-O-(iC15:0)-iC17:0, and both amide- and ester-linked (R)-3-OH C16:0. Fatty acid distribution analyses using several mass spectrometry determinations demonstrated that the former two constituents were distributed on positions 2 and 3 of the reducing terminal unit of the backbones and that the latter two were attached to the 2' and 3' positions in the nonreducing terminal residue.
Figures


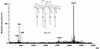
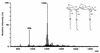


References
-
- Bednarski M, Danishefsky S. Interactivity of chiral catalysts and chiral auxiliaries in the cycloaddition of activated dienes with aldehydes: a synthesis of l-glucose. J Am Chem Soc. 1986;108:7060–7067.
-
- Brade H, Moll H, Rietschel E T. Structural investigations on the inner core region of lipopolysaccharides from Salmonella minnesota rough mutants. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1985;12:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan R E, Gibbons N E, editors. Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. 8th ed. Baltimore, Md: The Williams & Wilkins Co.; 1974. pp. 357–364.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

