The conjugal intermediate of plasmid RSF1010 inhibits Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence and VirB-dependent export of VirE2
- PMID: 9683491
- PMCID: PMC107378
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.15.3933-3939.1998
The conjugal intermediate of plasmid RSF1010 inhibits Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence and VirB-dependent export of VirE2
Abstract
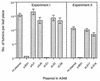
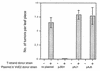
Agrobacterium tumefaciens causes crown gall disease by transferring oncogenic, single-stranded DNA (T strand), covalently attached to the VirD2 protein, across the bacterial envelope into plant cells where its expression results in tumor formation. The single-stranded DNA binding protein VirE2 is also transferred into the plant cell, though the location at which VirE2 interacts with the T strand is still under investigation. The movement of the transferred DNA and VirE2 from A. tumefaciens to the plant cell depends on the membrane-localized VirB and VirD4 proteins. Further, the movement of the IncQ broad-host-range plasmid RSF1010 between Agrobacterium strains or from Agrobacterium to plants also requires the virB-encoded transfer system. Our earlier studies showed that the presence of the RSF1010 plasmid in wild-type strains of Agrobacterium inhibits both their virulence and their capacity to transport VirE2, as assayed by coinfection with virE mutants. Here we demonstrate that the capacity to form a conjugal intermediate of RSF1010 is necessary for this inhibition, suggesting that the transferred form of the plasmid competes with the VirD2-T strand and/or VirE2 for a common export site.
Figures
References
-
- Bagdasarian M, Lurz R, Franklin F C H, Bagdasarian M M, Frey J, Timmis K N. Specific purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene. 1981;16:237–247. - PubMed
-
- Beijersbergen A, Dulk-Ras A D, Schilperoort R A, Hooykaas P J J. Conjugative transfer by the virulence system of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Science. 1992;256:1324–1327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

