A dual-signaling mechanism mediated by the ArcB hybrid sensor kinase containing the histidine-containing phosphotransfer domain in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 9683496
- PMCID: PMC107383
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.15.3973-3977.1998
A dual-signaling mechanism mediated by the ArcB hybrid sensor kinase containing the histidine-containing phosphotransfer domain in Escherichia coli
Abstract
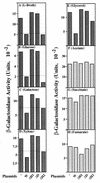
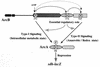
The two components ArcB and ArcA play a crucial role in the signal transduction implicated in the complex transcriptional regulatory network that allows Escherichia coli to sense various respiratory growth conditions. ArcB is a hybrid sensor kinase having multiple phosphorylation sites in its primary amino acid sequence, including a transmitter, a receiver, and a histidine-containing phosphotransfer (HPt) domain. ArcA is a DNA-binding transcriptional regulator with a receiver domain. Results of recent in vitro studies revealed multistep His-to-Asp phosphotransfer circuitry in the ArcB-ArcA signaling system. For this report we conducted a series of in vivo experiments using a set of crucial ArcB mutants to evaluate the regulation of the sdh operon. The results suggested that the phosphorylated His-717 site in the HPt domain of ArcB is essential for anaerobic repression of sdh. Nonetheless, the ArcB mutant lacking this crucial His-717 site does not necessarily exhibit a null phenotype with respect to ArcB-ArcA signaling. The HPt mutant appears to maintain an ability to signal ArcA, particularly under aerobic conditions, which results in a significant repression of sdh. Based on these and other in vivo results, we propose a model in which ArcB functions in its own right as a dual-signaling sensor that is capable of propagating two types of stimuli through two distinct phosphotransfer pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Appleby J L, Parkinson J S, Bourret R B. Signal transduction via the multi-step phosphorelay: not necessarily a road less traveled. Cell. 1996;86:845–848. - PubMed
-
- Hoch J A, Silhavy T J. Two-component signal transduction. Washington, D.C: ASM Press; 1995.
-
- Inouye M. His-Asp phosphorelay; two components or more? Cell. 1996;85:13–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

