Identification of OmpT as the protease that hydrolyzes the antimicrobial peptide protamine before it enters growing cells of Escherichia coli
- PMID: 9683502
- PMCID: PMC107389
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.15.4002-4006.1998
Identification of OmpT as the protease that hydrolyzes the antimicrobial peptide protamine before it enters growing cells of Escherichia coli
Abstract
The influence of extracytoplasmic proteases on the resistance of Escherichia coli to the antimicrobial peptide protamine was investigated by testing strains with deletions in the protease genes degP, ptr, and ompT. Only DeltaompT strains were hypersusceptible to protamine. This effect was abolished by plasmids carrying ompT. Both at low and at high Mg2+ concentrations, ompT+ strains cleared protamine from the medium within a few minutes. By contrast, at high Mg2+ concentrations, protamine remained present for at least 1 h in the medium of an ompT strain. These data indicate that OmpT is the protease that degrades protamine and that it exerts this function at the external face of the outer membrane.
Figures
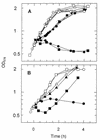
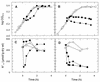
References
-
- Ando T, Watanabe S. A new method for fractionation of protamines and the amino acid sequences of one compound of salmine and three compounds of iridine. Int J Protein Res. 1969;1:221–224. - PubMed
-
- Ando T, Yamasaki M, Suzuki S. Protamines; isolation, characterization and function. New York, N.Y: Springer Verlag; 1973. pp. 58–80. - PubMed
-
- Aspedon A, Groisman E A. The antibacterial action of protamine: evidence for disruption of cytoplasmic membrane energization in Salmonella typhimurium. Microbiology. 1996;142:3389–3397. - PubMed
-
- Elish M E, Pierce J R, Earhart C F. Biochemical analysis of spontaneous fepA mutants of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1988;134:1355–1364. - PubMed
-
- Foxman B, Zhang L, Palin K, Tallmann P, Marrs C F. Bacterial virulence characteristics of Escherichia coli isolates from first time urinary tract infection. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:1514–1521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

