Parallel radiation hybrid mapping: a powerful tool for high-resolution genomic comparison
- PMID: 9685320
- PMCID: PMC310752
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.8.7.731
Parallel radiation hybrid mapping: a powerful tool for high-resolution genomic comparison
Abstract
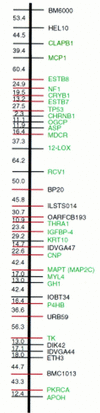
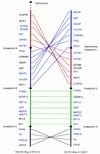
Comparative gene mapping in mammals typically involves identification of segments of conserved synteny in diverse genomes. The development of maps that permit comparison of gene order within conserved synteny has not advanced beyond the mouse map that takes advantage of linkage analysis in interspecific backcrosses. Radiation hybrid (RH) mapping provides a powerful tool for determining order of genes in genomes for which gene-based linkage mapping is impractical. Comparative RH mapping of 24 orthologous genes in this study revealed internal structural rearrangements between human chromosome 17 (HSA17) and bovine chromosome 19 (BTA19), two chromosomes known previously to be conserved completely and exclusively at level of synteny. Only six of the 24 genes had been previously ordered on the human G3 RH map. The use of the G3 panel to map the other 18, however, produced parallel RH maps for comparison of gene order at a resolution of <5 Mb on the bovine linkage map and from 1 to 3 Mb in the human physical map.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An integrated radiation hybrid map of bovine chromosome 19 and ordered comparative mapping with human chromosome 17.Genomics. 1998 Feb 15;48(1):93-9. doi: 10.1006/geno.1997.5143. Genomics. 1998. PMID: 9503021
-
A 12,000-rad porcine radiation hybrid (IMNpRH2) panel refines the conserved synteny between SSC12 and HSA17.Genomics. 2005 Dec;86(6):731-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.08.006. Epub 2005 Nov 11. Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16289748
-
High resolution radiation hybrid maps of bovine chromosomes 19 and 29: comparison with the bovine genome sequence assembly.BMC Genomics. 2007 Sep 4;8:310. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-310. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17784962 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative approach to physical and linkage mapping of genes on canine chromosomes using gene-associated simple sequence repeat polymorphisms illustrated by studies of dog chromosome 9.J Hered. 1999 Jan-Feb;90(1):39-42. doi: 10.1093/jhered/90.1.39. J Hered. 1999. PMID: 9987901 Review.
-
Development and applications of a molecular genetic linkage map of the mouse genome.Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):113-8. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90455-y. Trends Genet. 1991. PMID: 2068781 Review.
Cited by
-
Reconstructing the genomic architecture of mammalian ancestors using multispecies comparative maps.Hum Genomics. 2003 Nov;1(1):30-40. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-1-1-30. Hum Genomics. 2003. PMID: 15601531 Free PMC article.
-
A radiation hybrid map of the cat genome: implications for comparative mapping.Genome Res. 2000 May;10(5):691-702. doi: 10.1101/gr.10.5.691. Genome Res. 2000. PMID: 10810092 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA1: a new candidate gene for bovine mastitis and its association analysis between single nucleotide polymorphisms and milk somatic cell score.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Jun;39(6):6625-31. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1467-5. Epub 2012 Feb 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22327776
-
Comparative organization of cattle chromosome 5 revealed by comparative mapping by annotation and sequence similarity and radiation hybrid mapping.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Apr 11;97(8):4150-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.050007097. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10737760 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive conservation of sex chromosome organization between cat and human revealed by parallel radiation hybrid mapping.Genome Res. 1999 Dec;9(12):1223-30. doi: 10.1101/gr.9.12.1223. Genome Res. 1999. PMID: 10613845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barendse W, Vaiman D, Kemp SJ, Sugimoto Y, Armitage SM, Williams JL, Sun HS, Eggen A, Agaba M, Aleyasin SA, et al. A medium-density genetic linkage map of the bovine genome. Mamm Genome. 1997;8:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Boehnke M. Multipoint analysis for radiation hybrid mapping. Ann Med. 1992;24:383–386. - PubMed
-
- Carver EA, Stubbs L. Zooming in on the human–mouse comparative map: Genome conservation re-examined on a high-resolution scale. Genome Res. 1997;7:1123–1137. - PubMed
-
- Chowdhary BP, Fronicke L, Gustavsson I, Scherthan H. Comparative analysis of the cattle and human genomes: Detection of ZOO-FISH and gene mapping-based chromosomal homologies. Mamm Genome. 1996;7:297–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
