Y-688, a new quinolone active against quinolone-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: lack of in vivo efficacy in experimental endocarditis
- PMID: 9687379
- PMCID: PMC105705
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.8.1889
Y-688, a new quinolone active against quinolone-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: lack of in vivo efficacy in experimental endocarditis
Abstract
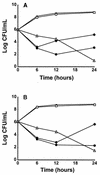
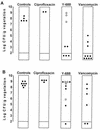
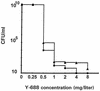
Y-688 is a new fluoroquinolone with increased activity against ciprofloxacin-resistant staphylococci. The MICs of Y-688 and other quinolones were determined for 58 isolates of ciprofloxacin-resistant and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The MICs at which 50% and 90% of bacteria were inhibited were >/=128 and >/=128 mg/liter, respectively, for ciprofloxacin, 16 and 32 mg/liter, respectively, for sparfloxacin, and 0.25 and 1 mg/liter, respectively, for Y-688. This new quinolone was further tested in rats with experimental endocarditis due to either of two isolates of ciprofloxacin-resistant MRSA (namely, P8/128 and CR1). Infected animals were treated for 3 days with ciprofloxacin, vancomycin, or Y-688. Antibiotics were administered through a computerized pump to simulate human-like pharmacokinetics in the serum of rats. The anticipated peak and trough levels of Y-688 were 4 and 1 mg/liter at 0.5 and 12 h, respectively. Treatment with ciprofloxacin was ineffective. Vancomycin significantly decreased vegetation bacterial counts for both organisms (P less, similar 0.05). In contrast, Y-688 only marginally decreased vegetation bacterial counts (P greater, similar 0.05). Moreover, several vegetation that failed Y-688 treatment grew staphylococci for which the MICs of the test antibiotic were increased two to eight times. Y-688 also selected for resistance in vitro, and isolates for which the MICs were increased eight times emerged at a frequency of ca. 10(-8). Thus, in spite of its low MIC for ciprofloxacin-resistant MRSA, Y-688 failed in vivo and its use carried the risk of resistance selection. The fact that ciprofloxacin-resistant staphylococci became rapidly resistant to this potent new drug suggests that the treatment of ciprofloxacin-resistant MRSA with new quinolones might be more problematic than expected.
Figures
References
-
- Borner K, Höffken G, Lode H, Koeppe P, Prinzing C, Glatzel P, Wiley R, Olschewski P, Sievers B, Reinitz D. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin in healthy volunteers after oral and intravenous administration. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986;5:179–186. - PubMed
-
- Cremieux A C, Maziere B, Vallois J M, Ottaviani M, Azancot A, Raffoul H, Bouvet A, Pocidalo J J, Carbon C. Evaluation of antibiotic diffusion into cardiac vegetations by quantitative autoradiography. J Infect Dis. 1989;159:938–944. - PubMed
-
- Crémieux A C, Saleh-Mghir A, Vallois J M, Ottaviani M, Pocidalo J J, Carbon C. Program and abstracts of the 31st Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1991. Pattern and diffusion of three quinolones throughout infected cardiac vegetations studied by autoradiography, abstr. 357; p. 158.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

