Overexpression of the marA or soxS regulatory gene in clinical topoisomerase mutants of Escherichia coli
- PMID: 9687412
- PMCID: PMC105868
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.8.2089
Overexpression of the marA or soxS regulatory gene in clinical topoisomerase mutants of Escherichia coli
Abstract
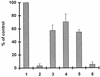
The contribution of regulatory genes to fluoroquinolone resistance was studied with clinical Escherichia coli strains bearing mutations in gyrA and parC and with different levels of fluoroquinolone resistance. Expression of marA and soxS was evaluated by Northern blot analysis of isolates that demonstrated increased organic solvent tolerance, a phenotype that has been linked to overexpression of marA, soxS, and rob. Among 25 cyclohexane-tolerant strains detected by a screen for increased organic solvent tolerance (M. Oethinger, W. V. Kern, J. D. Goldman, and S. B. Levy, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 41:111-114, 1998), we found 5 Mar mutants and 4 Sox mutants. A further Mar mutant was detected among 11 fluoroquinolone-resistant, cyclohexane-susceptible E. coli strains used as controls. Comparison of the marOR sequences of clinical Mar mutants with that of E. coli K-12 (GenBank accession no. M96235) revealed point mutations in marR in all mutants which correlated with loss of repressor function as detected in a marO::lacZ transcriptional assay. We found four other amino acid changes in MarR that did not lead to loss of function. Two of these changes, present in 20 of the 35 sequenced marOR fragments, identified a variant genotype of marOR. Isolates with the same gyrA and parC mutations showed increased fluoroquinolone resistance when the mutations were accompanied by overexpression of marA or soxS. These data support the hypothesis that high-level fluoroquinolone resistance involves mutations at several chromosomal loci, comprising structural and regulatory genes.
Figures
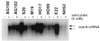
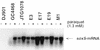
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

