Regulation of B cell development by variable gene complexity in mice reconstituted with human immunoglobulin yeast artificial chromosomes
- PMID: 9687526
- PMCID: PMC2212477
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.3.483
Regulation of B cell development by variable gene complexity in mice reconstituted with human immunoglobulin yeast artificial chromosomes
Abstract
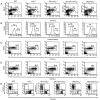
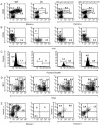
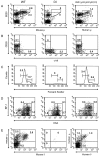
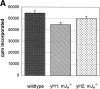
The relationship between variable (V) gene complexity and the efficiency of B cell development was studied in strains of mice deficient in mouse antibody production and engineered with yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) containing different sized fragments of the human heavy (H) chain and kappa light (L) chain loci. Each of the two H and the two kappa chain fragments encompasses, in germline configuration, the same core variable and constant regions but contains different numbers of unique VH (5 versus 66) or Vkappa genes (3 versus 32). Although each of these YACs was able to substitute for its respective inactivated murine counterpart to induce B cell development and to support production of human immunoglobulins (Igs), major differences in the efficiency of B cell development were detected. Whereas the YACs with great V gene complexity restored efficient development throughout all the different recombination and expression stages, the YACs with limited V gene repertoire exhibited inefficient differentiation with significant blocks at critical stages of B cell development in the bone marrow and peripheral lymphoid tissues. Our analysis identified four key checkpoints regulated by VH and Vkappa gene complexity: (a) production of functional mu chains at the transition from the pre B-I to the pre B-II stage; (b) productive VkappaJkappa recombination at the small pre B-II stage; (c) formation of surface Ig molecules through pairing of mu chains with L chains; and (d) maturation of B cells. These findings demonstrate that V gene complexity is essential not only for production of a diverse repertoire of antigen-specific antibodies but also for efficient development of the B cell lineage.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Analysis of the structural integrity of YACs comprising human immunoglobulin genes in yeast and in embryonic stem cells.Genomics. 1995 Mar 20;26(2):294-307. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80214-7. Genomics. 1995. PMID: 7601456
-
Production of antigen-specific human antibodies from mice engineered with human heavy and light chain YACs.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Sep 29;764:525-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb55878.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. PMID: 7486581
-
Early rearrangements of genes encoding murine immunoglobulin kappa chains, unlike genes encoding heavy chains, use variable gene segments dispersed throughout the locus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6744-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6744. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989. PMID: 2505260 Free PMC article.
-
Revising B cell receptors.J Exp Med. 2000 Jun 5;191(11):1813-7. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.11.1813. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10839798 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Molecular genetics of immunoglobulins.Immunol Suppl. 1988;1:7-15. Immunol Suppl. 1988. PMID: 3133312 Review.
Cited by
-
The super-information age of immunoglobulin genetics.J Exp Med. 1998 Dec 7;188(11):1973-5. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.11.1973. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9841911 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Human antibody production in transgenic animals.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2015 Apr;63(2):101-8. doi: 10.1007/s00005-014-0322-x. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2015. PMID: 25467949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human monoclonal antibodies against Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide derived from transgenic mice containing megabase human immunoglobulin loci are opsonic and protective against fatal pseudomonas sepsis.Infect Immun. 2001 Apr;69(4):2223-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2223-2229.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11254577 Free PMC article.
-
Progress and Challenges in the Design and Clinical Development of Antibodies for Cancer Therapy.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 4;8:1751. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01751. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29379493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A human immunoglobulin lambda locus is similarly well expressed in mice and humans.J Exp Med. 1999 May 17;189(10):1611-20. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.10.1611. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10330440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hardy RR, Hayakawa K. B-lineage differentiation stages resolved by multiparameter flow cytometry. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1995;764:19–24. - PubMed
-
- Rolink A, Melchers F. B-cell development in the mouse. Immunol Lett. 1996;54:157–161. - PubMed
-
- Loffert A, Schaal S, Ehlich A, Hardy RR, Zou Y-R, Muller W, Rajewsky K. Early B-cell development in the mouse: insights from mutations introduced by gene targeting. Immunol Rev. 1994;137:135–154. - PubMed
-
- Nussenzweig MC, Shaw AC, Sinn E, Danner DB, Holmes KL, Morse HC, III, Leder P. Allelic exclusion in transgenic mice that express the membrane form of immunoglobulin μ. Science. 1987;236:816–819. - PubMed
-
- Hartley SB, Cooke MP, Fulcher DA, Harris AW, Cory S, Basten A, Goodnow CC. Elimination of self-reactive B lymphocytes proceeds in two stages: arrested development and cell death. Cell. 1993;72:325–335. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

